EGFR variant allele frequency predicts EGFR-TKI efficacy in lung adenocarcinoma: a multicenter study
- PMID: 33718012
- PMCID: PMC7947383
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-20-814
EGFR variant allele frequency predicts EGFR-TKI efficacy in lung adenocarcinoma: a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: Although lung adenocarcinoma (LADC) with sensitizing mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is highly sensitive to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs), in most cases disease progression inevitably occurs. Our aim was to investigate the predictive and prognostic significance of adjusted tumoral EGFR variant allele frequency (EGFR-aVAF) in the above setting.
Methods: Eighty-nine Caucasian advanced-stage LADC patients with known exon-specific EGFR mutations undergoing EGFR-TKI treatment were included. The correlations of EGFR-aVAF with clinicopathological variables including progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS, respectively) were retrospectively analyzed.
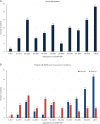
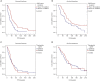
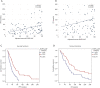
Results: Of 89 EGFR-mutant LADC patients, 46 (51.7%) had exon 19 deletion, while 41 (46.1%) and 2 (2.2%) patients had exon 21- and exon 18-point mutations, respectively. Tumoral EGFR-aVAF was significantly higher in patients harboring EGFR exon 19 mutations than in those with exon 21-mutant tumors (P<0.001). Notably, patients with EGFR exon 19 mutant tumors demonstrated significantly improved PFS (P=0.003) and OS (P=0.02) compared to patients with exon 21 mutations. Irrespective of specific exon mutations, a statistically significant positive linear correlation was found between EGFR-aVAF of tumoral tissue and PFS (r=0.319; P=0.002). High (≥70%) EGFR-aVAF was an independent predictor of longer PFS [vs. low (<70%) EGFR-aVAF; median PFSs were 52 vs. 26 weeks, respectively; P<0.001]. Additionally, patients with high EGFR-aVAF also had significantly improved OS than those with low EGFR-aVAF (P=0.011).
Conclusions: Our study suggests that high (≥70%) EGFR-aVAF of tumoral tissue predicts benefit from EGFR-TKI treatment in advanced LADC and, moreover, that exon 19 EGFR mutation is associated with high EGFR-aVAF and improved survival outcomes.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation (EGFR mutation); lung adenocarcinoma (LADC); variant allele frequency (VAF).
2021 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-814). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
