Latest CT technologies in lung cancer screening: protocols and radiation dose reduction
- PMID: 33718053
- PMCID: PMC7947397
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-20-808
Latest CT technologies in lung cancer screening: protocols and radiation dose reduction
Erratum in
-
Erratum to latest CT technologies in lung cancer screening: protocols and radiation dose reduction.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Apr;10(4):2101-2102. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-2021-2. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34012818 Free PMC article.
Abstract
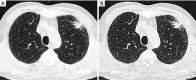
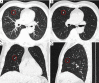
The aim of this review is to provide clinicians and technicians with an overview of the development of CT protocols in lung cancer screening. CT protocols have evolved from pre-fixed settings in early lung cancer screening studies starting in 2004 towards automatic optimized settings in current international guidelines. The acquisition protocols of large lung cancer screening studies and guidelines are summarized. Radiation dose may vary considerably between CT protocols, but has reduced gradually over the years. Ultra-low dose acquisition can be achieved by applying latest dose reduction techniques. The use of low tube current or tin-filter in combination with iterative reconstruction allow to reduce the radiation dose to a submilliSievert level. However, one should be cautious in reducing the radiation dose to ultra-low dose settings since performed studies lacked generalizability. Continuous efforts are made by international radiology organizations to streamline the CT data acquisition and image quality assurance and to keep track of new developments in CT lung cancer screening. Examples like computer-aided diagnosis and radiomic feature extraction are discussed and current limitations are outlined. Deep learning-based solutions in post-processing of CT images are provided. Finally, future perspectives and recommendations are provided for lung cancer screening CT protocols.
Keywords: Lung cancer; computed tomography; radiation dose reduction; screening.
2021 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-20-808). The series “Implementation of CT-based screening of lung cancer” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. Dr. MV reports other from IDNA B.V., outside the submitted work. Dr. RV reports grants from Siemens Healthineers, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Kim Y. Implementation of organized lung cancer screening program in Korea. Ann Oncol 2019;30:ii14. 10.1093/annonc/mdz070 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
