Relationship between the risk factors of cardiovascular disease by testing biochemical markers and young men with erectile dysfunction: a case-control study
- PMID: 33718074
- PMCID: PMC7947441
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-20-1056
Relationship between the risk factors of cardiovascular disease by testing biochemical markers and young men with erectile dysfunction: a case-control study
Abstract
Background: Erectile dysfunction (ED) shares common risk factors with cardiovascular disease (CVD), such as diabetes mellitus (DM) and dyslipidemia, but the relationship between the risk factors of CVD in biochemical markers and young men with ED age 20-40 years is not fully clarified.
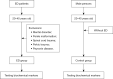
Methods: A total of 289 ED outpatients (20-40 years old) were allocated under ED group, based on patients' complaints and physical examinations. According to the frequency matching ratio of 1:4, 1,155 male individuals (20-40 years old) without ED were set as control group. All participants were tested for lipid profiles including total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high density lipoprotein (HDL), low density lipoprotein (LDL), blood glucose (BG), homocysteine (HCY), liver function including alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and renal function including uric acid (UA) and creatinine (CR). The study was designed to compare the two groups using an established binary logistic regression analysis model. The ED group was then subdivided into a younger ED group (20-30 years old) and an older ED group (31-40 years old) for further comparisons.
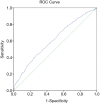
Results: After comparison, no obvious differences were found in medians of age, TC, TG, HDL, HCY, UA, and ALT in the two groups. Median LDL, BG, and CR were significantly higher and AST was much lower in the ED group (P<0.01). In binary logistic regression analysis, odds ratios (OR) for LDL, BG, CR, and AST were 1.279, 1.237, 1.026, and 0.978, respectively. The sensitivity value and specificity value were 43.25% and 72.56%, respectively. The medians of LDL, TG, and TC were higher and HDL was much lower in the older ED group, as compared with the younger group (P<0.05). No significant differences were displayed in medians of other biochemical markers in the above comparisons.
Conclusions: Elevated LDL, BG, and CR were related factors of ED in young men. Lipid profile was significantly different between young men with ED aged 20-30 and 31-40 years.
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction (ED); case-control study; lipid profile.
2021 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-1056). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of fatty liver disease in the elderly.Exp Gerontol. 2013 Aug;48(8):705-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.05.059. Epub 2013 May 27. Exp Gerontol. 2013. PMID: 23721951
-
[Study on the relationship between WBC count levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Hui and Han nationality of Ningxia].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2015 May;44(3):387-92. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2015. PMID: 26137615 Chinese.
-
Significance of blood lipid parameters as effective markers for arteriogenic erectile dysfunction.Andrology. 2020 Sep;8(5):1086-1094. doi: 10.1111/andr.12776. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Andrology. 2020. PMID: 32087037
-
AST to ALT ratio and arterial stiffness in non-fatty liver Japanese population:a secondary analysis based on a cross-sectional study.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Dec 3;17(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0920-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30509277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the serum lipid profile in prediction of diabetic neuropathy.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):499. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79276-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33436718 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Insights into modifiable risk factors of erectile dysfunction, a wide-angled Mendelian Randomization study.J Adv Res. 2024 Apr;58:149-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.05.008. Epub 2023 May 25. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37236543 Free PMC article.
-
Association between atorvastatin and erectile dysfunction: a comprehensive analysis incorporating real-world pharmacovigilance and Mendelian randomization.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 29;15:1382924. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1382924. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38741592 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine, Vitamin B12 and Folate Level: Possible Risk Factors in the Progression of Chronic Heart and Kidney Disorders.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2023;19(4):e090223213539. doi: 10.2174/1573403X19666230209111854. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36757031 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum homocysteine and erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Impot Res. 2025 Aug;37(8):574-582. doi: 10.1038/s41443-024-00978-4. Epub 2024 Nov 30. Int J Impot Res. 2025. PMID: 39616259
-
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide ameliorated diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction in rats by regulating fibrosis and the NOS/ERK/JNK pathway.Transl Androl Urol. 2022 Jul;11(7):982-995. doi: 10.21037/tau-22-428. Transl Androl Urol. 2022. PMID: 35958898 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous