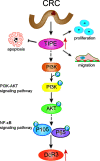
TIPE Regulates DcR3 Expression and Function by Activating the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in CRC
- PMID: 33718119
- PMCID: PMC7943851
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.623048
TIPE Regulates DcR3 Expression and Function by Activating the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in CRC
Abstract
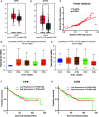
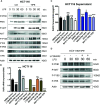
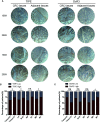
Tumor necrosis factor-induced protein-8 (TIPE) is highly expressed in colorectal cancer (CRC). Decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) is a soluble secreted protein that can antagonize Fas ligand (FasL)-induced apoptosis and promote tumorigenesis. It remains unclear whether TIPE can regulate DcR3 expression. In this study, we examined this question by analyzing the relationship between these factors in CRC. Bioinformatics and tissue microarrays were used to determine the expression of TIPE and DcR3 and their correlation in CRC. The expression of TIPE and DcR3 in colon cancer cells was detected. Plasma samples were collected from CRC patients, and DcR3 secretion was measured. Then, dual-luciferase reporter gene analysis was performed to assess the interaction between TIPE and DcR3. We exogenously altered TIPE expression and analyzed its function and influence on DcR3 secretion. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used to stimulate TIPE-overexpressing HCT116 cells, and alterations in signaling pathways were detected. Additionally, inhibitors were used to confirm molecular mechanisms. We found that TIPE and DcR3 were highly expressed in CRC patients and that their expression levels were positively correlated. DcR3 was highly expressed in the plasma of cancer patients. We confirmed that TIPE and DcR3 were highly expressed in HCT116 cells. TIPE overexpression enhanced the transcriptional activity of the DcR3 promoter. TIPE activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to regulate the expression of DcR3, thereby promoting cell proliferation and migration and inhibiting apoptosis. In summary, TIPE and DcR3 are highly expressed in CRC, and both proteins are associated with poor prognosis. TIPE regulates DcR3 expression by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in CRC, thus promoting cell proliferation and migration and inhibiting apoptosis. These findings may have clinical significance and promise for applications in the treatment or prognostication of CRC.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; apoptosis; cell proliferation; colorectal cancer; migration.
Copyright © 2021 Zhong, Qiu, Liu, Yang, Gu, Wang, Chen, Liu, Miao and Zhuang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of tumor necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8 in stage III gastric cancer and the correlation with DcR3 and ERK1/2.Oncol Lett. 2016 Mar;11(3):1835-1840. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4133. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26998086 Free PMC article.
-
TIPE regulates VEGFR2 expression and promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan 1;16(2):272-283. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.37906. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31929755 Free PMC article.
-
Decoy receptor 3 expression in AsPC-1 human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-, Akt-, and NF-kappa B-dependent pathway.J Immunol. 2008 Dec 15;181(12):8441-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8441. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19050262
-
Decoy receptor 3: an endogenous immunomodulator in cancer growth and inflammatory reactions.J Biomed Sci. 2017 Jun 19;24(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12929-017-0347-7. J Biomed Sci. 2017. PMID: 28629361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoy receptor 3: a pleiotropic immunomodulator and biomarker for inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases and cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 1;81(7):838-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.011. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21295012 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress of DcR3 in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Sepsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 18;24(16):12916. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612916. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-539 activates the SAPK/JNK signaling pathway to promote ferropotosis in colorectal cancer by directly targeting TIPE.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Oct 2;7(1):272. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00659-x. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34601499 Free PMC article.
-
The Network of Pro-Inflammatory Factors CD147, DcR3, and IL33 in the Development of Kawasaki Disease.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Nov 19;14:6043-6053. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S338763. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34824540 Free PMC article.
-
Oxymatrine inhibits the development of radioresistance in NSCLC cells by reversing EMT through the DcR3/AKT/GSK-3β pathway.Arch Med Sci. 2023 Jan 5;20(5):1631-1654. doi: 10.5114/aoms/158533. eCollection 2024. Arch Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 39649262 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the genetic landscape of susceptibility to multiple primary cancers.HGG Adv. 2025 Apr 10;6(2):100413. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2025.100413. Epub 2025 Feb 4. HGG Adv. 2025. PMID: 39910817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel S, Wang FH, Whiteside TL, Kasid U. Identification of seven differentially displayed transcripts in human primary and matched metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines: implications in metastasis and/or radiation response. Oral Oncol (1997) 33:197–203. 10.1016/s0964-1955(96)00065-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

