The Prognostic Value of Circulating Soluble Programmed Death Ligand-1 in Cancers: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33718120
- PMCID: PMC7950317
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.626932
The Prognostic Value of Circulating Soluble Programmed Death Ligand-1 in Cancers: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Studies on the prognostic value of the soluble programmed death ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in cancer patients have not yielded consistent results.
Objective: This meta-analysis was performed to assess the association between sPD-L1 and the prognosis of cancer patients.
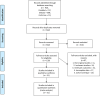
Methods: Published articles in Pubmed, EMBASE, and Cochrane clinical trial databases were searched from the inception to September 2020. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), recurrence-free survival (RFS), and disease-free survival (DFS) data were evaluated using a hazard ratio (HR) at 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
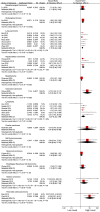
Results: A total 31 studies involving 17 tumors and 3,780 patients were included. The overexpression of sPD-L1 was associated with shorter OS (HR 1.85, 95% CI 1.59-2.15, I2 = 33%). High sPD-L1 had worse PFS (HR 2.40, 95% CI 1.55-3.72, I2 = 83%), and worse DFS (HR 2.92, 95% CI 2.02-4.29, I2 = 40%), without significant statistical difference in RFS (HR 2.08, 95% CI 0.99-4.40, I2 = 0%).
Conclusions: High sPD-L1 levels were associated with worse survival prognosis in cancer patients. The sPD-L1 may be a potential prognostic, non-invasive, and dynamic monitoring biomarker for cancers in the future.
Keywords: cancers; meta-analysis; prognosis; soluble programmed death ligand 1; survival.
Copyright © 2021 Huang, Hu, Zhu, Wu and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic Value of Soluble Programmed Cell Death Ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in Various Cancers: A Meta-analysis.Target Oncol. 2021 Jan;16(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s11523-020-00763-5. Target Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33222017
-
Prognostic value of soluble programmed cell death-1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022 Jul;71(7):1633-1644. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03103-2. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022. PMID: 34750662 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of the prognostic value of soluble programmed death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in cancers.Biomarkers. 2023 Sep;28(6):477-485. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2023.2198168. Epub 2023 Jul 2. Biomarkers. 2023. PMID: 37017446
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2458236. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2458236. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39928126 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Values of Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Expression for Prognosis, Clinicopathological Factors, and Response to Programmed Cell Death-1/Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Inhibitors in Patients With Gynecological Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 1;10:572203. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.572203. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33634012 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
High Pretreatment Serum PD-L1 Levels Are Associated with Muscle Invasion and Shorter Survival in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 13;10(10):2560. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102560. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289821 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Role of Soluble Programmed Death Ligand 1 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 23;11:774131. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.774131. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35004295 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-treatment soluble PD-L1 as a predictor of overall survival for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 May;72(5):1061-1073. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03328-9. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36385210 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed Cell Death-Ligand-1 expression in Bladder Schistosomal Squamous Cell Carcinoma - There's room for Immune Checkpoint Blockage?.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 2;13:955000. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955000. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36148227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progresses in biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Oct 3;4(5):e387. doi: 10.1002/mco2.387. eCollection 2023 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37799808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takahashi N, Iwasa S, Sasaki Y, Shoji H, Honma Y, Takashima A, et al. . Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 as a prognostic factor on the first-line treatment of metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol (2016) 142(8):1727–38. 10.1007/s00432-016-2184-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

