A CT-Based Radiomics Approach to Predict Nivolumab Response in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33718125
- PMCID: PMC7943844
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.544339
A CT-Based Radiomics Approach to Predict Nivolumab Response in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to develop a CT-based radiomics model to predict clinical outcomes of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with nivolumab.
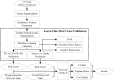
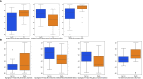
Methods: Forty-six stage IIIB/IV NSCLC patients without EGFR mutation or ALK rearrangement who received nivolumab were enrolled. After segmenting primary tumors depicting on the pre-anti-PD1 treatment CT images, 1,106 radiomics features were computed and extracted to decode the imaging phenotypes of these tumors. A L1-based feature selection method was applied to remove the redundant features and build an optimal feature pool. To predict the risk of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), the selected image features were used to train and test three machine-learning classifiers namely, support vector machine classifier, logistic regression classifier, and Gaussian Naïve Bayes classifier. Finally, the overall patients were stratified into high and low risk subgroups by using prediction scores obtained from three classifiers, and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conduct to evaluate the prognostic values of these patients.
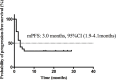
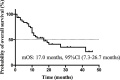
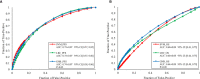
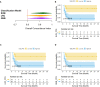
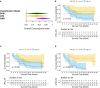
Results: To predict the risk of PFS and OS, the average area under a receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) value of three classifiers were 0.73 ± 0.07 and 0.61 ± 0.08, respectively; the corresponding average Harrell's concordance indexes for three classifiers were 0.92 and 0.79. The average hazard ratios (HR) of three models for predicting PFS and OS were 6.22 and 3.54, which suggested the significant difference of the two subgroup's PFS and OS (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The pre-treatment CT-based radiomics model provided a promising way to predict clinical outcomes for advanced NSCLC patients treated with nivolumab.
Keywords: CT-based radiomics approach; NSCLC; immunotherapy; machine-learning; nivolumab.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Gong, Yu, Liu, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, et al. . Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet (2017) 389:255–65. 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)32517-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

