Epigenetic Silencing of STAT3-Targeted miR-193a, by Constitutive Activation of JAK/STAT Signaling, Leads to Tumor Progression Through Overexpression of YWHAZ in Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 33718136
- PMCID: PMC7951088
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.575667
Epigenetic Silencing of STAT3-Targeted miR-193a, by Constitutive Activation of JAK/STAT Signaling, Leads to Tumor Progression Through Overexpression of YWHAZ in Gastric Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to identify genes that were epigenetically silenced by STAT3 in gastric cancer.
Methods: MBDcap-Seq and expression microarray were performed to identify genes that were epigenetically silenced in AGS gastric cancer cell lines depleted of STAT3. Cell lines and animal experiments were performed to investigate proliferation and metastasis of miR-193a and YWHAZ in gastric cancer cell lines. Bisulfite pyrosequencing and tissue microarray were performed to investigate the promoter methylation of miR-193a and expression of STAT3, YWHAZ in patients with gastritis (n = 8) and gastric cancer (n = 71). Quantitative methylation-specific PCR was performed to examine miR-193a promoter methylation in cell-free DNA of serum samples in gastric cancer patients (n = 19).
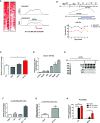
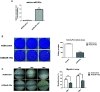
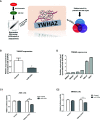
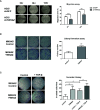
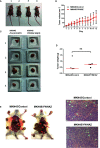
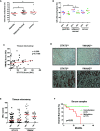
Results: As compared with parental cells, depletion of STAT3 resulted in demethylation of a putative STAT3 target, miR-193a, in AGS gastric cancer cells. Although bisulfite pyrosequencing and epigenetic treatment confirmed that miR-193a was epigenetically silenced in gastric cancer cell lines, ChIP-PCR found that it may be indirectly affected by STAT3. Ectopic expression of miR-193a in AGS cells inhibited proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Further expression microarray and bioinformatics analysis identified YWHAZ as one of the target of miR-193a in AGS gastric cancer cells, such that depletion of YWHAZ reduced migration in AGS cells, while its overexpression increased invasion in MKN45 cells in vitro and in vivo. Clinically, bisulfite pyrosequencing revealed that promoter methylation of miR-193a was significantly higher in human gastric cancer tissues (n = 11) as compared to gastritis (n = 8, p < 0.05). Patients infected with H. pylori showed a significantly higher miR-193a methylation than those without H. pylori infection (p < 0.05). Tissue microarray also showed a positive trend between STAT3 and YWHAZ expression in gastric cancer patients (n = 60). Patients with serum miR-193a methylation was associated with shorter overall survival than those without methylation (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Constitutive activation of JAK/STAT signaling may confer epigenetic silencing of the STAT3 indirect target and tumor suppressor microRNA, miR-193a in gastric cancer. Transcriptional suppression of miR-193a may led to overexpression of YWHAZ resulting in tumor progression. Targeted inhibition of STAT3 may be a novel therapeutic strategy against gastric cancer.
Keywords: STAT3; YWHAZ; epigenetics; gastric cancer; miR-193a.
Copyright © 2021 Wei, Chou, Chen, Low, Lin, Liu, Chang, Chen, Hsieh, Yan, Chuang, Lin, Wu, Chiang, Li, Wu and Chan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic silencing of the NR4A3 tumor suppressor, by aberrant JAK/STAT signaling, predicts prognosis in gastric cancer.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 16;6:31690. doi: 10.1038/srep31690. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27528092 Free PMC article.
-
Methylomics analysis identifies a putative STAT3 target, SPG20, as a noninvasive epigenetic biomarker for early detection of gastric cancer.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 13;14(6):e0218338. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218338. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31194837 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant JAK/STAT Signaling Suppresses TFF1 and TFF2 through Epigenetic Silencing of GATA6 in Gastric Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 2;17(9):1467. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091467. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27598141 Free PMC article.
-
Methylomic analysis identifies C11orf87 as a novel epigenetic biomarker for GI cancers.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 22;16(4):e0250499. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250499. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33886682 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation-associated silencing of miR-193a-3p promotes ovarian cancer aggressiveness by targeting GRB7 and MAPK/ERK pathways.Theranostics. 2018 Jan 1;8(2):423-436. doi: 10.7150/thno.22377. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29290818 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The global prevalence of gastric cancer in Helicobacter pylori-infected individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Aug 19;23(1):543. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08504-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37598157 Free PMC article.
-
PCDHB15 as a potential tumor suppressor and epigenetic biomarker for breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2022 Apr;23(4):117. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13237. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35261631 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of NF1 microdeletions and its importance for establishing genotype/phenotype correlations in patients with NF1 microdeletions.Hum Genet. 2021 Dec;140(12):1635-1649. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02363-3. Epub 2021 Sep 18. Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34535841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blaser MJ, Perez-Perez GI, Kleanthous H, Cover TL, Peek RM, Chyou PH, et al. . Infection with Helicobacter pylori strains possessing cagA is associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res (1995) 55:2111–5. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

