Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Changes of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Biomarkers for Patients With Pancreatic Cancer Treated With Immune Checkpoint Blockade
- PMID: 33718140
- PMCID: PMC7943876
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.585271
Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index and Changes of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Biomarkers for Patients With Pancreatic Cancer Treated With Immune Checkpoint Blockade
Abstract
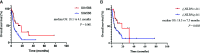
The efficacy of current treatment regimens for pancreatic cancer (PC) remains unsatisfactory. In recent years, immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy has shown promising anti-tumor outcomes in many malignancies, including PC. Inexpensive and readily available biomarkers which predict therapeutic responses and prognosis are in critical need. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) are emerging predictors for prognosis of various tumors. We aim to investigate the prognostic significance of baseline SII, NLR, and their changes in PC patients treated with ICB. Our retrospective analysis included PC patients treated with ICB therapy in the Chinese PLA General Hospital. All demographic, biological, and clinical data were extracted from medical records. Relative changes of SII after two doses of ICB were defined as ΔSII% and calculated as (SIIafter 2 doses-SIIbaseline)/SIIbaseline, and so was the case for ΔNLR%. Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were compared using Kaplan-Meier curves. The prognostic significance of baseline SII, NLR, and their changes was assessed in univariate and multivariate analyses using the Cox proportional hazard regression model. In total, 122 patients with PC treated with ICB were included in the present analysis. Elevated baseline SII (HR=3.28; 95% CI:1.98-5.27; P=0.03) and ΔNLR% (HR=2.21; 95% CI:1.03-4.74; P=0.04) were significantly correlated with an increased risk of death. For PC patients receiving ICB combined with chemotherapies or radiotherapies as the first-line treatment, increased baseline SII was a negative predictor for both OS (HR=8.06; 95% CI:1.71-37.86; P=0.01) and PFS (HR=2.84; 95%CI:1.37-10.38; P=0.04). Our study reveals the prognostic value of baseline SII and NLR changes in PC patients receiving ICB therapy. The clinical utility of these prognostic biomarkers needs to be further studied in prospective studies.
Keywords: immune checkpoint blockade; immunotherapy; neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; pancreatic cancer; prognosis; systemic immune-inflammation index.
Copyright © 2021 Shang, Han, Zha, Tao, Li, Yuan, Chen, Wang, Ma and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
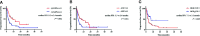

Similar articles
-
Systemic immune-inflammation index, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio can predict clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Oct;33(8):e22964. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22964. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 31282096 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Predicting Survival Outcomes in Patients with Brain Metastases of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Stereotactic Radiotherapy.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Oct 29;2021:2910892. doi: 10.1155/2021/2910892. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34744510 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of immunotherapy-induced inflammation indexes: dynamic changes in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2280002. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2280002. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 38065623 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic utility of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review and meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Feb 23;11:955-965. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S153290. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29503570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of the systemic immune-inflammation index in pancreatic carcinoma patients: a meta-analysis.Biosci Rep. 2021 Aug 27;41(8):BSR20204401. doi: 10.1042/BSR20204401. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34286342 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Complete Blood Count-Derived Inflammatory Markers Changes in Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy Treated with Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;12(20):2798. doi: 10.3390/ani12202798. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290184 Free PMC article.
-
The Predictive Value of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index on Bladder Recurrence on Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Outcomes after Radical Nephroureterectomy.J Clin Med. 2021 Nov 12;10(22):5273. doi: 10.3390/jcm10225273. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34830555 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma in First Line Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 1;11(3):749. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030749. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979727 Free PMC article.
-
Directing T-Cell Immune Responses for Cancer Vaccination and Immunotherapy.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;9(12):1392. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121392. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The predictive value of inflammatory biomarkers for major pathological response in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy and its association with the immune-related tumor microenvironment: a multi-center study.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Mar;72(3):783-794. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03262-w. Epub 2022 Sep 3. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36056951 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

