Compound C, a Broad Kinase Inhibitor Alters Metabolic Fingerprinting of Extra Cellular Matrix Detached Cancer Cells
- PMID: 33718166
- PMCID: PMC7947618
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.612778
Compound C, a Broad Kinase Inhibitor Alters Metabolic Fingerprinting of Extra Cellular Matrix Detached Cancer Cells
Abstract
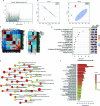
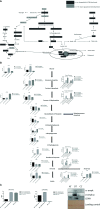
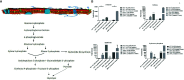
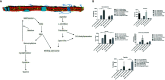
Most of the cancer related deaths are caused mainly by metastasis. Therefore, it is highly important to unfold the major mechanisms governing metastasis process in cancer. Throughout the metastatic cascade, cells need the ability to survive without attachment to neighboring cells and the original Extra Cellular Matrix (ECM). Recent reports showed that loss of ECM attachment shifts cancer cell metabolism towards glycolysis mostly through hypoxia. However, AMPK, a master metabolic regulator was also found to be upregulated under ECM detached conditions. Therefore, in this work we aimed to understand the consequences of targeting AMPK and other metabolic kinases by a broad kinase inhibitor namely Compound C in ECM detached cancer cells. Results showed that Compound C impacts glycolysis as evident by increased levels of pyruvate, but reduces its conversion to lactate thereby negatively regulating the Warburg effect. Simultaneously, Compound C induces block at multiple levels in TCA cycle as evident from accumulation of various TCA metabolites. Interestingly Compound C significantly reduces glutamine and reduced glutathione levels, suggesting loss of antioxidant potential of ECM detached cancer cells. Further, we found increased in metabolites associated with nucleotide synthesis, one carbon metabolism and PPP pathway during Compound C treatment of ECM detached cells. Finally, we also found induction in metabolites associated with DNA damage in ECM detached cancer cells during Compound C treatment, suggesting DNA damage regulatory role of metabolic kinases. Overall, our results showed that Compound C represses pyruvate to lactate conversion, reduces antioxidant potential and invokes DNA damage in ECM detached cancer cells. Our data provides a comprehensive metabolic map of ECM detached cancer cells that can be targeted with a broad kinase inhibitor, is Compound C. The data can be used for designing new combinational therapies to eradicate ECM detached cancer cells.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; compound C; extra cellular matrix detachment; metabolomic analysis; oxidative phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2021 Shait Mohammed, Alghamdi, Alzahrani, Zamzami, Choudhry and Khan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

