Tumor Decelerating and Chemo-Potentiating Action of Methyl Jasmonate on a T Cell Lymphoma In Vivo: Role of Altered Regulation of Metabolism, Cell Survival, Drug Resistance, and Intratumoral Blood Flow
- PMID: 33718176
- PMCID: PMC7947686
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.619351
Tumor Decelerating and Chemo-Potentiating Action of Methyl Jasmonate on a T Cell Lymphoma In Vivo: Role of Altered Regulation of Metabolism, Cell Survival, Drug Resistance, and Intratumoral Blood Flow
Abstract
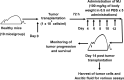
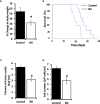
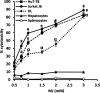
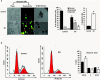
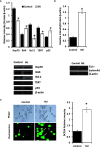
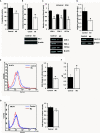
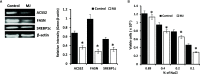
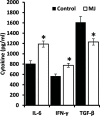
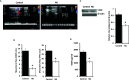
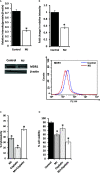
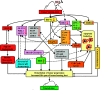
Methyl jasmonate (MJ), a natural oxylipin, possesses a broad spectrum of antineoplastic potential in vitro. However, its tumor growth impeding and chemo-potentiating action has not been adequately investigated in vivo. Using a murine thymus-derived tumor named Dalton's Lymphoma (DL), in the present study, we examined if intra-tumoral administration of MJ can cause tumor growth impedance. We also explored the associated molecular mechanisms governing cell survival, carbohydrate & lipid metabolism, chemo-potentiation, and angiogenesis. MJ administration to tumor-transplanted mice caused deceleration of tumor growth accompanying prolonged survival of the tumor-bearing mice. MJ-dependent tumor growth retardation was associated with the declined blood supply in tumor milieu, cell cycle arrest, augmented induction of apoptosis and necrosis, deregulated glucose and lipid metabolism, enhanced membrane fragility of tumor cells, and altered cytokine repertoire in the tumor microenvironment. MJ administration modulated molecular network implicating Hsp70, Bcl-2, TERT, p53, Cyt c, BAX, GLUT-1, HK 2, LDH A, PDK-1, HIF-1α, ROS, MCT-1, FASN, ACSS2, SREBP1c, VEGF, cytokine repertoire, and MDR1, involved in the regulation of cell survival, carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism, pH homeostasis, and drug resistance. Thus, the present study unveils novel molecular mechanisms of the tumor growth decelerating action of MJ. Besides, this preclinical study also establishes the adjunct therapeutic potential of MJ. Hence, the present investigation will help to design novel anti-cancer therapeutic regimens for the treatment of hematological malignancies.
Keywords: cell survival and metabolic regulation; chemo-potentiation; intra-tumoral blood flow; methyl jasmonate; tumor growth impedance.
Copyright © 2021 Goel, Yadav, Pandey, Temre, Maurya, Verma, Kumar and Singh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glutor, a Glucose Transporter Inhibitor, Exerts Antineoplastic Action on Tumor Cells of Thymic Origin: Implication of Modulated Metabolism, Survival, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, pH Homeostasis, and Chemosensitivity.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:925666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.925666. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847943 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl Jasmonate Cytotoxicity and Chemosensitization of T Cell Lymphoma In Vitro Is Facilitated by HK 2, HIF-1α, and Hsp70: Implication of Altered Regulation of Cell Survival, pH Homeostasis, Mitochondrial Functions.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 26;12:628329. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.628329. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33716751 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor growth retardation and chemosensitizing action of fatty acid synthase inhibitor orlistat on T cell lymphoma: implication of reconstituted tumor microenvironment and multidrug resistance phenotype.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1840(1):294-302. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.09.020. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24060750
-
Methyl jasmonate: putative mechanisms of action on cancer cells cycle, metabolism, and apoptosis.Int J Cell Biol. 2014;2014:572097. doi: 10.1155/2014/572097. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Int J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24648844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jasmonates--a new family of anti-cancer agents.Anticancer Drugs. 2005 Oct;16(9):911-6. doi: 10.1097/01.cad.0000176501.63680.80. Anticancer Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16162967 Review.
Cited by
-
Orchestral role of lipid metabolic reprogramming in T-cell malignancy.Front Oncol. 2023 May 15;13:1122789. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1122789. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37256177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reprogramming lipid metabolism as potential strategy for hematological malignancy therapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;12:987499. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.987499. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36106108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EZH2 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in human uterine fibroids, which is inhibited by the natural compound methyl jasmonate.F S Sci. 2023 Aug;4(3):239-256. doi: 10.1016/j.xfss.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 May 12. F S Sci. 2023. PMID: 37182601 Free PMC article.
-
Glutor, a Glucose Transporter Inhibitor, Exerts Antineoplastic Action on Tumor Cells of Thymic Origin: Implication of Modulated Metabolism, Survival, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Membrane Potential, pH Homeostasis, and Chemosensitivity.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:925666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.925666. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847943 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Jasmonic Acid and Its Derivatives.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 5;22(16):8437. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168437. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

