Upregulation of PEDF Predicts a Poor Prognosis and Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Modulating the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33718190
- PMCID: PMC7953146
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.625612
Upregulation of PEDF Predicts a Poor Prognosis and Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Modulating the MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
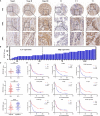
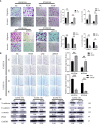
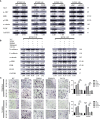
Invasion and metastasis represent the primary causes of therapeutic failure in patients diagnosed with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The lack of effective treatment strategies for metastatic ESCC is the major cause of the low survival rate. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying ESCC metastasis and identify potential biomarkers for targeted therapy. Herein, we reported that PEDF is significantly correlated with tumor cell invasion and metastasis in ESCC. The high expression of PEDF is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor for ESCC patients' overall survival (OS). We successfully developed and verified a nomogram to predict the preoperative OS of ESCC patients, and the actual and nomogram-predicted 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates had good consistency. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve showed that the area under the curve (AUC) values for 1-, 3- and 5- survival were 0.764, 0.871, and 0.91, respectively. Overexpression of PEDF significantly promoted the migration and invasion of ESCC cells in vitro, while silencing PEDF yielded the opposite effects. Elevated levels of PEDF altered the expression of proteins involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), as indicated by the upregulation of N-cadherin and the downregulation of α-catenin and E-cadherin in ESCC cells. Mechanistically, PEDF promoted tumor cell motility and EMT by activating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. In conclusion, our results reveal that PEDF is involved in ESCC metastasis and could act as a prognostic factor for ESCC. Our research provides a fresh perspective into the mechanism of ESCC metastasis.
Keywords: MAPK/ERK; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; metastasis; pigment epithelium-derived factor; prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Che, Gu, Lin, Deng, Jiang, Xu, Xu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

