The Most Efficacious Induction Chemotherapy Regimen for Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33718193
- PMCID: PMC7951057
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626145
The Most Efficacious Induction Chemotherapy Regimen for Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Induction chemotherapy (IC) followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) for non-metastatic locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) has gained considerable attention. However, the most efficacious IC regimens remain investigational. We aimed to compare the survival benefits of all available IC regimens followed by CCRT in this network meta-analysis.
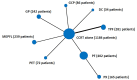
Methods: All randomized-controlled trials of CCRT with or without IC in non-metastatic locoregionally advanced NPC were included, with an overall nine trials of 2,705 patients counted in the analysis. CCRT alone was the reference category. Eight IC regimens followed by CCRT were analyzed: docetaxel + cisplatin (DC), gemcitabine + carboplatin + paclitaxel (GCP), gemcitabine + cisplatin (GP), mitomycin + epirubicin + cisplatin + fluorouracil + leucovorin (MEPFL), cisplatin + epirubicin + paclitaxel (PET), cisplatin + fluorouracil (PF), cisplatin + capecitabine (PX) and cisplatin + fluorouracil (PF), cisplatin + capecitabine (PX). Fixed-effects frequentist network meta-analysis models was applied and P-score was used to rank the treatments.
Results: DC, GP, and PX were the top three IC regimens with the highest probability of benefit on overall survival (OS). Their corresponding hazard ratios (HRs) (95% CIs) compared with CCRT alone were of 0.24 (0.08-0.73), 0.43 (0.24-0.77), and 0.54 (0.27-1.09) and the respective P-scores were 94%, 82%, and 68%. The first three IC regimens showing significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) were PX, followed by GP and DC with respective HRs of 0.46 (0.24-0.88), 0.51 (0.34-0.77), and 0.49 (0.20-1.20), and P-scores of 82%, 78%, and 74%. Among the studies in the intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) era, GP and PX were the best performed IC regimens, whilst DC performed the best among non-IMRT studies. Doublet and gemcitabine-based IC regimens had better survival benefits compared to triplet and taxane-based IC regimens, respectively.
Conclusions: Given its consistent superiority in both OS and PFS, DC, GP, and PX ranked among the three most efficacious IC regimens in both the overall and subgroup analysis of IMRT or non-IMRT studies. Exploratory analyses suggested that doublet and gemcitabine-based IC regimens showed better survival performance.
Keywords: efficacy; induction chemotherapy; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; network meta-analysis; survival outcome.
Copyright © 2021 Choi, Chan, Lam, Chan, Chau, Kwong, Leung, Luk, Lee and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of three induction chemotherapy regimens with gemcitabine plus cisplatin (GP), cisplatin plus fluorouracil (PF) and cisplatin plus capecitabine (PX) for locoregionally advanced previously untreated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A pooled analysis of two prospective studies.Oral Oncol. 2021 Mar;114:105158. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.105158. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Oral Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33508707
-
The efficacy and safety of docetaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil (TPF)-based induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2020 Mar;22(3):429-439. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02142-7. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Clin Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31165410
-
The safety and efficacy of gemcitabine and cisplatin (GP)-based induction chemotherapy plus concurrent chemoradiotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Mar;279(3):1561-1572. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06940-0. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34259896
-
Long-term outcomes of induction chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiotherapy and adjuvant chemotherapy for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective study.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 27;14:1475176. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1475176. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39664180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pretreatment Plasma EBV-DNA Load Guides Induction Chemotherapy Followed by Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 16;10:610787. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.610787. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33665166 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of TPF and PF induction chemotherapy combined with cisplatin concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jan 17;104(3):e41278. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041278. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39833074 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the efficacy and safety of cisplatin and other platinum-based chemotherapies in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 6;22(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09712-z. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35668431 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Current and Emerging Treatment Options.Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Sep 12;14:2681-2689. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S341472. eCollection 2022. Cancer Manag Res. 2022. PMID: 36117730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Single-Arm Phase 2 Trial on Induction Chemotherapy Followed by Concurrent Chemoradiation in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Using a Reduced Cumulative Dose of Cisplatin.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 27;12:842281. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.842281. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35574402 Free PMC article.
-
An Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes and Associated Factors in Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients at a Tertiary Cancer Center in the United Arab Emirates.Cureus. 2024 Feb 17;16(2):e54344. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54344. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38371438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) . Global Cancer Observatory, World Health Organization, 2020(2020). Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/ (Accessed September 20, 2020).
-
- Petit C, Lee AWM, Carmel A, Ng WT, Ma J, Cjhan ATC, et al. . Network-meta-analysis of chemotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (MAC-NPC): An update on 8,221 patients. J Clin Oncol (2020) 38(Suppl; abstr 6523). 10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15 - DOI
-
- Lee AW, Ngan RK, Tung SY, Cheng A, Kwong DLW, Lu T, et al. . Preliminary results of trial NPC-0501 evaluating the therapeutic gain by changing from concurrent-adjuvant to induction-concurrent chemoradiotherapy, changing from fluorouracil to capecitabine, and changing from conventional to accelerated radiotherapy fractionation in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer (2015) 121:1328–38. 10.1002/cncr.29208 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

