MR-Guided Adaptive Radiotherapy for Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 33718230
- PMCID: PMC7947660
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.637591
MR-Guided Adaptive Radiotherapy for Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Radiotherapy has an important role in the curative and palliative treatment settings for bladder cancer. As a target for radiotherapy the bladder presents a number of technical challenges. These include poor tumor visualization and the variability in bladder size and position both between and during treatment delivery. Evidence favors the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as an important means of tumor visualization and local staging. The availability of hybrid systems incorporating both MRI scanning capabilities with the linear accelerator (MR-Linac) offers opportunity for in-room and real-time MRI scanning with ability of plan adaption at each fraction while the patient is on the treatment couch. This has a number of potential advantages for bladder cancer patients. In this article, we examine the technical challenges of bladder radiotherapy and explore how magnetic resonance (MR) guided radiotherapy (MRgRT) could be leveraged with the aim of improving bladder cancer patient outcomes. However, before routine clinical implementation robust evidence base to establish whether MRgRT translates into improved patient outcomes should be ascertained.
Keywords: MR guided radiotherapy; MR-linac; MRI; adaptive radiotherapy; bladder cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Hijab, Tocco, Hanson, Meijer, Nyborg, Bertelsen, Smeenk, Smith, Michalski, Baumann and Hafeez.
Conflict of interest statement
BCB reports personal fees from Mevion, personal fees from Mevion/Sanofi, outside the submitted work. SH reports non-financial support from Elekta (Elekta AB, Stockholm, Sweden), non-financial support from Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), personal fees and non-financial support from Roche outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
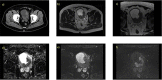
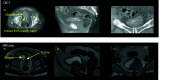
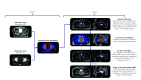
References
-
- Advanced Bladder Cancer Meta-analysis C . Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. Eur Urol (2005) 48(2):202–205; discussion 205-206. 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.04.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gakis G, Efstathiou J, Lerner SP, Cookson MS, Keegan KA, Guru KA, et al. . ICUD-EAU International Consultation on Bladder Cancer 2012: Radical cystectomy and bladder preservation for muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol (2013) 63(1):45–57. 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.08.009 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

