Molecular Epidemiology and Clone Transmission of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in ICU Rooms
- PMID: 33718283
- PMCID: PMC7952536
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.633817
Molecular Epidemiology and Clone Transmission of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in ICU Rooms
Abstract
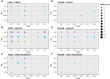
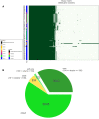
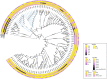
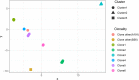
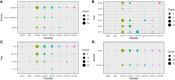
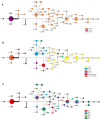
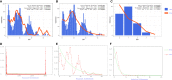
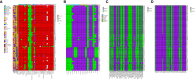
Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) is a major cause of nosocomial infections and hospital outbreaks worldwide, remaining a critical clinical concern. Here we characterized and investigated the phylogenetic relationships of 105 CRAB isolates from an intensive care unit from one hospital in China collected over six years. All strains carried blaOXA-23 , blaOXA-66 genes for carbapenem resistance, also had high resistance gene, virulence factor, and insertion sequence burdens. Whole-genome sequencing revealed all strains belonged to ST2, the global clone CC2. The phylogenetic analysis based on the core genome showed all isolates were dominated by a single lineage of three clusters and eight different clones. Two clones were popular during the collection time. Using chi-square test to identify the epidemiologically meaningful groupings, we found the significant difference in community structure only existed in strains from separation time. The haplotype and median-joining network analysis revealed genetic differences appeared among clusters and changes occurred overtime in the dominating cluster. Our results highlighted substantial multidrug-resistant CRAB burden in the hospital ICU environment demonstrating potential clone outbreak in the hospital.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; carbapenem-resistant; clone spread; nosocomial infection; whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Li, Awan, Jiang, Zeng and Lv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phenotypic and molecular characterization of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates causing lower respiratory infections among ICU patients.Microb Pathog. 2019 Mar;128:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.12.023. Epub 2018 Dec 15. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30562602
-
Epidemiological and genetic characteristics of clinical carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains collected countrywide from hospital intensive care units (ICUs) in China.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022 Dec;11(1):1730-1741. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2093134. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022. PMID: 35730377 Free PMC article.
-
Accumulation of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Belonging to Lineage 2, Global Clone 1, from Outbreaks in 2012-2013 at a Tehran Burns Hospital.mSphere. 2020 Apr 8;5(2):e00164-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00164-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32269158 Free PMC article.
-
Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A challenge in the intensive care unit.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1045206. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1045206. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36439795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Burden of severe infections due to carbapenem-resistant pathogens in intensive care unit.World J Clin Cases. 2023 May 6;11(13):2874-2889. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i13.2874. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37215420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Community and Genomic Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from the Environment of a Health Care Facility in the Western Region of Saudi Arabia.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 16;15(5):611. doi: 10.3390/ph15050611. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631436 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes and risk factors of Acinetobacter baumannii meningitis in pediatric patients at a tertiary hospital in China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 29;14:1408959. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1408959. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39268489 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and oxacillinase OXA distribution characteristics of Acinetobacter spp. based on a global database.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 1;14:1174200. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1174200. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37323896 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome analysis revealed the role of blaOXA-23 and blaOXA-66 genes in carbapenem resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii strains.Pathog Glob Health. 2025 Feb-Mar;119(1-2):10-21. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2024.2442194. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Pathog Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 39699991
-
Preferential Selection of Low-Frequency, Lipopolysaccharide-Modified, Colistin-Resistant Mutants with a Combination of Antimicrobials in Acinetobacter baumannii.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0192822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01928-22. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36173297 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

