COVID-19: Rethinking the Lockdown Groupthink
- PMID: 33718322
- PMCID: PMC7952324
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.625778
COVID-19: Rethinking the Lockdown Groupthink
Abstract
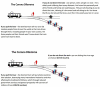
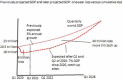
The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) worldwide pandemic in 2020. In response, most countries in the world implemented lockdowns, restricting their population's movements, work, education, gatherings, and general activities in attempt to "flatten the curve" of COVID-19 cases. The public health goal of lockdowns was to save the population from COVID-19 cases and deaths, and to prevent overwhelming health care systems with COVID-19 patients. In this narrative review I explain why I changed my mind about supporting lockdowns. The initial modeling predictions induced fear and crowd-effects (i.e., groupthink). Over time, important information emerged relevant to the modeling, including the lower infection fatality rate (median 0.23%), clarification of high-risk groups (specifically, those 70 years of age and older), lower herd immunity thresholds (likely 20-40% population immunity), and the difficult exit strategies. In addition, information emerged on significant collateral damage due to the response to the pandemic, adversely affecting many millions of people with poverty, food insecurity, loneliness, unemployment, school closures, and interrupted healthcare. Raw numbers of COVID-19 cases and deaths were difficult to interpret, and may be tempered by information placing the number of COVID-19 deaths in proper context and perspective relative to background rates. Considering this information, a cost-benefit analysis of the response to COVID-19 finds that lockdowns are far more harmful to public health (at least 5-10 times so in terms of wellbeing years) than COVID-19 can be. Controversies and objections about the main points made are considered and addressed. Progress in the response to COVID-19 depends on considering the trade-offs discussed here that determine the wellbeing of populations. I close with some suggestions for moving forward, including focused protection of those truly at high risk, opening of schools, and building back better with a economy.
Keywords: COVID-19; cost-benefit analysis; groupthink; lockdowns; public health.
Copyright © 2021 Joffe.
Conflict of interest statement
Theauthor declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar A, Qureshi S, Reynolds S, Light RB, Sligl W, Bates A, et al. Opinion: All Levels of Government Must Take Decision, Co-ordinated Action Now - Before It's Too Late: A Group of Physicians Trained in Both Infectious Diseases and Critical Care Medicine Discuss What Canadian Governments Must Do to Prevent This Country From Finding Itself in a Similar Situation to What Italy and Spain Are Experiencing. The National Post. (2020) Available online at: https://nationalpost.com/opinion/opinion-all-levels-of-government-must-t... (accessed October 11, 2020).
-
- Kissler SM, Tedijanto C, Lipsitch M, Grad Y. Social distancing strategies for curbing the COVID-19 epidemic. medRxiv [Preprint]. (2020). 10.1101/2020.03.22.20041079 - DOI
-
- Ferguson NM, Laydon D, Nedjati-Gilani G, Imai N, Ainslie K, Baguelin M, et al. Report 9: Impact of Non-pharmaceutical Interventions (NPIs) to Reduce COVID-19 Mortality and Healthcare Demand. (2020) Available online at: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/mrc-global-infectious-disease-analysis/covid-... (accessed October 11, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

