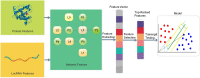
Prediction of lncRNA-Protein Interactions via the Multiple Information Integration
- PMID: 33718346
- PMCID: PMC7947871
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.647113
Prediction of lncRNA-Protein Interactions via the Multiple Information Integration
Abstract
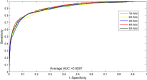
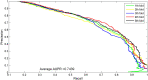
The long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-protein interaction plays an important role in the post-transcriptional gene regulation, such as RNA splicing, translation, signaling, and the development of complex diseases. The related research on the prediction of lncRNA-protein interaction relationship is beneficial in the excavation and the discovery of the mechanism of lncRNA function and action occurrence, which are important. Traditional experimental methods for detecting lncRNA-protein interactions are expensive and time-consuming. Therefore, computational methods provide many effective strategies to deal with this problem. In recent years, most computational methods only use the information of the lncRNA-lncRNA or the protein-protein similarity and cannot fully capture all features to identify their interactions. In this paper, we propose a novel computational model for the lncRNA-protein prediction on the basis of machine learning methods. First, a feature method is proposed for representing the information of the network topological properties of lncRNA and protein interactions. The basic composition feature information and evolutionary information based on protein, the lncRNA sequence feature information, and the lncRNA expression profile information are extracted. Finally, the above feature information is fused, and the optimized feature vector is used with the recursive feature elimination algorithm. The optimized feature vectors are input to the support vector machine (SVM) model. Experimental results show that the proposed method has good effectiveness and accuracy in the lncRNA-protein interaction prediction.
Keywords: feature representation; lncRNA protein interactions; mutual information; structure analysis; support vector machine.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Fu, Li, Peng and Zhuo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Projection-Based Neighborhood Non-Negative Matrix Factorization for lncRNA-Protein Interaction Prediction.Front Genet. 2019 Nov 20;10:1148. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01148. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31824563 Free PMC article.
-
LDNFSGB: prediction of long non-coding rna and disease association using network feature similarity and gradient boosting.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Sep 3;21(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-03721-0. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32883200 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting lncRNA-disease associations using network topological similarity based on deep mining heterogeneous networks.Math Biosci. 2019 Sep;315:108229. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2019.108229. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Math Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31323239
-
Recent Advances on the Semi-Supervised Learning for Long Non-Coding RNA-Protein Interactions Prediction: A Review.Protein Pept Lett. 2020;27(5):385-391. doi: 10.2174/0929866526666191025104043. Protein Pept Lett. 2020. PMID: 31654509 Review.
-
Recent advances in machine learning methods for predicting LncRNA and disease associations.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 30;12:1071972. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1071972. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36530425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction of Plant Resistance Proteins Based on Pairwise Energy Content and Stacking Framework.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 31;13:912599. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.912599. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35712582 Free PMC article.
-
MILNP: Plant lncRNA-miRNA Interaction Prediction Based on Improved Linear Neighborhood Similarity and Label Propagation.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 25;13:861886. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.861886. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35401586 Free PMC article.
-
LPI-deepGBDT: a multiple-layer deep framework based on gradient boosting decision trees for lncRNA-protein interaction identification.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Oct 4;22(1):479. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04399-8. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34607567 Free PMC article.
-
ET-PROTACs: modeling ternary complex interactions using cross-modal learning and ternary attention for accurate PROTAC-induced degradation prediction.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Nov 22;26(1):bbae654. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae654. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39783892 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-Protein Interactions: A Key to Deciphering LncRNA Mechanisms.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 17;15(6):881. doi: 10.3390/biom15060881. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bai Y., Dai X., Ye T., Zhang P., Yan X., Gong X., et al. . (2019). PlncRNADB: a repository of plant lncRNAs and lncRNA-RBP protein interactions. Curr. Bioinform. 14, 621–627. 10.2174/1574893614666190131161002 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources