Integrated Protein-Protein Interaction and Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis Uncover Three Key Genes in Hepatoblastoma
- PMID: 33718368
- PMCID: PMC7953069
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.631982
Integrated Protein-Protein Interaction and Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis Uncover Three Key Genes in Hepatoblastoma
Abstract
Hepatoblastoma (HB) is the most common liver tumor in the pediatric population, with typically poor outcomes for advanced-stage or chemotherapy-refractory HB patients. The objective of this study was to identify genes involved in HB pathogenesis via microarray analysis and subsequent experimental validation. We identified 856 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between HB and normal liver tissue based on two publicly available microarray datasets (GSE131329 and GSE75271) after data merging and batch effect correction. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) were conducted to explore HB-related critical modules and hub genes. Subsequently, Gene Ontology (GO) analysis was used to reveal critical biological functions in the initiation and progression of HB. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis showed that genes involved in cell cycle phase transition and the PI3K/AKT signaling were associated with HB. The intersection of hub genes identified by both PPI and WGCNA analyses revealed five potential candidate genes. Based on receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and reports in the literature, we selected CCNA2, CDK1, and CDC20 as key genes of interest to validate experimentally. CCNA2, CDK1, or CDC20 small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown inhibited aggressive biological properties of both HepG2 and HuH-6 cell lines in vitro. In conclusion, we identified CCNA2, CDK1, and CDC20 as new potential therapeutic biomarkers for HB, providing novel insights into important and viable targets in future HB treatment.
Keywords: CCNA2; CDC20; CDK1; PPI; WGCNA; hepatoblastoma.
Copyright © 2021 Tian, Chen, Lu, Yan, Zhang, Qin, Ding and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

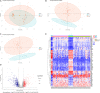





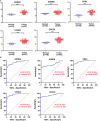

References
-
- Bandettini W. P., Kellman P., Mancini C., Booker O. J., Vasu S., Leung S. W., et al. (2012). MultiContrast delayed enhancement (MCODE) improves detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a clinical validation study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 14:83. 10.1186/1532-429X-14-83 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

