COVID-19 and Risk of Acute Ischemic Stroke and Acute Lung Injury in Patients With Type II Diabetes Mellitus: The Anti-inflammatory Role of Metformin
- PMID: 33718411
- PMCID: PMC7944640
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.644295
COVID-19 and Risk of Acute Ischemic Stroke and Acute Lung Injury in Patients With Type II Diabetes Mellitus: The Anti-inflammatory Role of Metformin
Abstract
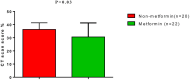
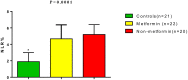
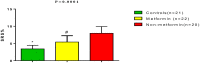
Background: Coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is regarded as an independent risk factor for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) due to the induction of endothelial dysfunction, coagulopathy, cytokine storm, and plaque instability. Method: In this retrospective cohort study, a total of 42 COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who presented with AIS within 1 week of displaying COVID-19 symptoms were recruited. According to the current anti-DM pharmacotherapy, patients were divided into two groups: a Metformin group of T2DM patients with COVID-19 and AIS on metformin therapy (850 mg, 3 times daily (n = 22), and a Non-metformin group of T2DM patients with COVID-19 and AIS under another anti-DM pharmacotherapy like glibenclamide and pioglitazone (n = 20). Anthropometric, biochemical, and radiological data were evaluated. Results: Ferritin serum level was lower in metformin-treated patients compared to non-metformin treated patients (365.93 ± 17.41 vs. 475.92 ± 22.78 ng/mL, p = 0.0001). CRP, LDH, and D-dimer serum levels were also lowered in metformin-treated patients compared to non-metformin treated patients (p = 0.0001). In addition, lung CT scan scores of COVID-19 patients was 30.62 ± 10.64 for metformin and 36.31 ± 5.03 for non-metformin treated patients. Conclusion: Metformin therapy in T2DM patients was linked to a lower risk of AIS during COVID-19. Further studies are needed to observe the link between AIS in COVID-19 diabetic patients and metformin therapy.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; acute ischaemic stroke; diabates mellitus; metformin.
Copyright © 2021 Al-kuraishy, Al-Gareeb, Alblihed, Cruz-Martins and Batiha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Naimi MS, Lungnier CM, Al-Gareeb AI. Macrolides and COVID-19: an optimum premise. Biomed Biotechnol Res J. (2020) 4:189. 10.4103/bbrj.bbrj_103_20 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

