Role of MicroRNAs in Protective Effects of Forsythoside A Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Bovine Endometrial Stromal Cells
- PMID: 33718475
- PMCID: PMC7943879
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2021.642913
Role of MicroRNAs in Protective Effects of Forsythoside A Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Bovine Endometrial Stromal Cells
Abstract
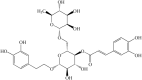
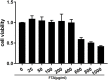
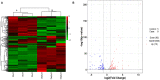
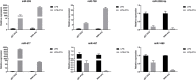
Bovine endometrial stromal cells (bESCs) are exposed to a complex environment of bacteria and viruses due to the rupture of epithelial cells after delivery. Inflammatory responses are elicited by the activation of host pattern recognition receptors through pathogen-related molecules such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) on the cell membrane. Forsythoside A (FTA) is a major active constituent of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl. is a flowering plant widely employed as a traditional Chinese herbal medicine to treat various inflammatory diseases such as nephritis, eye swelling, scabies, ulcers, and mastitis; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects on bovine endometritis are still unclear. The aim of this study was to explore the role of miRNA and the mechanisms underlying the protective activity of FTA on the inflammation of bovine endometrial stromal cells induced by LPS. Based on previous research, we isolated and cultured bESCs in vitro and categorized them into LPS and LPS+FTA groups with three replicates. Upon reaching 80% confluence, the bESCs were treated with 0.5 μg/mL of LPS or 0.5 μg/mL of LPS + 100 μg/mL of FTA. We, then, performed high-throughput sequencing (RNA-Seq) to investigate the effects of FTA on LPS-stimulated primary bESCs and their underlying mechanisms. We identified 167 miRNAs differentially expressed in the LPS groups; 72 miRNAs were up-regulated, and 95 were down-regulated. Gene ontology enrichment analysis revealed that differentially expressed microRNA (DEGs) were most enriched during the cellular metabolic process; they were mostly located intracellularly and participated in protein, enzyme, and ion binding. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis revealed that the DEGs were most enriched in the mitogen-activated protein kinase, tumor necrosis factor, and Interleukin-17 signaling pathways. These results reveal the complex molecular mechanism involved in the FTA and provide a basis for future studies of bovine endometritis treatment with traditional Chinese medicine monomer.
Keywords: bovine endometrial stromal cells; endometritis; forsythoside A; lipopolysaccharide; microRNA.
Copyright © 2021 Lv, Yan, Deng, Peng, Yang, Hu, Ding, Tong and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic profiling of lipopolysaccharide-challenged bovine mammary epithelial cells treated with forsythoside A.Anim Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;34(9):4523-4537. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2023.2165936. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Anim Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36651589
-
Analysis of miRNA expression changes in bovine endometrial stromal cells treated with lipopolysaccharide.Theriogenology. 2021 Jun;167:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.03.012. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Theriogenology. 2021. PMID: 33784501
-
Analysis of Transcriptomic Changes in Bovine Endometrial Stromal Cells Treated With Lipopolysaccharide.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Nov 26;7:575865. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.575865. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33324700 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and future research of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:318-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.040. Epub 2017 Sep 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28887216 Review.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates LPS-stimulated inflammatory response by regulating the PPARγ/NF-κB pathways in primary bovine mammary epithelial cells.Res Vet Sci. 2017 Jun;112:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Res Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28095338 Review.
Cited by
-
Forsythiaside A ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via anti-inflammation and antiapoptotic effects by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Feb 3;23(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03855-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36737765 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Study on the Alleviation of Endometritis in Mice Through Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways by Berberine and Carvacrol.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 30;13(5):1051. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13051051. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431224 Free PMC article.
-
Baogong decoction treats endometritis in mice by regulating uterine microbiota structure and metabolites.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 Nov;15(11):2786-2799. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14127. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35932174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cronin JG, Turner ML, Goetze L, Bryant CE, Sheldon IM. Toll-like receptor 4 and MYD88-dependent signaling mechanisms of the innate immune system are essential for the response to lipopolysaccharide by epithelial and stromal cells of the bovine endometrium. Biol Reprod. (2012) 86:51. 10.1095/biolreprod.111.092718 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

