Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials
- PMID: 33718505
- PMCID: PMC7930657
- DOI: 10.1177/2325967120973284
Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials
Abstract
Background: The effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections for knee osteoarthritis and the effects of leukocyte-poor PRP (LP-PRP) versus leukocyte-rich PRP (LR-PRP) are still controversial.
Purpose: To assess the effectiveness of different PRP injections through a direct and indirect meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Study design: Systematic review; Level of evidence, 1.
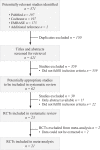
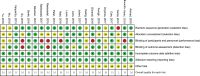
Methods: A systematic literature search of electronic databases (PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE) was performed to locate randomized controlled trials published through March 2019 that compared PRP with control treatment. A random-effects meta-analysis was conducted to synthesize the evidence, and meta-regression analyses were conducted to determine the influence of trial characteristics. An indirect comparison was performed to assess the effects of LP-PRP and LR-PRP compared with hyaluronic acid (HA).
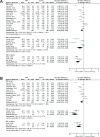
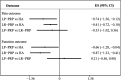
Results: A total of 21 trials were included. A clinically important benefit for pain relief was seen for intra-articular PRP compared with intra-articular saline (standardized mean difference [SMD] = -1.38 [95% CI, -2.07 to -0.70]; P < .0001; I 2 = 37%) and corticosteroid solution injection (SMD = -2.47 [95% CI, -3.34 to -1.61]; P < .00001; I 2 = 47%). As a result of heterogeneity (I 2 = 89%), there was no conclusive effect compared with HA, even though the pooling effect provided clinically relevant pain relief (SMD = -0.59 [95% CI, -0.97 to -0.21]; P = .003). Indirect meta-analysis showed that there was no significant difference between LR-PRP and LP-PRP.
Conclusion: PRP injections are beneficial for pain relief and functional improvement in knee osteoarthritis. Larger, randomized high-quality studies are needed to compare the effects of LP-PRP and LR-PRP.
Keywords: knee osteoarthritis; meta-analysis; platelet-rich plasma; randomized controlled clinical trials; treatment.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest in the authorship and publication of this contribution. AOSSM checks author disclosures against the Open Payments Database (OPD). AOSSM has not conducted an independent investigation on the OPD and disclaims any liability or responsibility relating thereto.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmad HS, Farrag SE, Okasha AE, et al. Clinical outcomes are associated with changes in ultrasonographic structural appearance after platelet-rich plasma treatment for knee osteoarthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21:960–966. - PubMed
-
- Andia I, Maffulli N. Platelet-rich plasma for managing pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9:721–730. - PubMed
-
- Buendía-López D, Medina-Quirós M, Fernández-Villacañas Marín MÁ. Clinical and radiographic comparison of a single LP-PRP injection, a single hyaluronic acid injection and daily NSAID administration with a 52-week follow-up: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Traumatol. 2018;19:3. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cerza F, Carni S, Carcangiu A, et al. Comparison between hyaluronic acid and platelet-rich plasma, intra-articular infiltration in the treatment of gonarthrosis. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40:2822–2827. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

