Applications of nuclear-based imaging in gene and cell therapy: probe considerations
- PMID: 33718593
- PMCID: PMC7907215
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.01.017
Applications of nuclear-based imaging in gene and cell therapy: probe considerations
Abstract
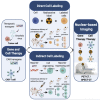
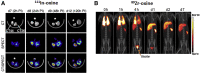
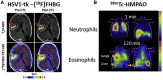
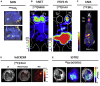
Several types of gene- and cell-based therapeutics are now emerging in the cancer immunotherapy, transplantation, and regenerative medicine landscapes. Radionuclear-based imaging can be used as a molecular imaging tool for repetitive and non-invasive visualization as well as in vivo monitoring of therapy success. In this review, we discuss the principles of nuclear-based imaging and provide a comprehensive overview of its application in gene and cell therapy. This review aims to inform investigators in the biomedical field as well as clinicians on the state of the art of nuclear imaging, from probe design to available radiopharmaceuticals and advances of direct (probe-based) and indirect (transgene-based) strategies in both preclinical and clinical settings. Notably, as the nuclear-based imaging toolbox is continuously expanding, it will be increasingly incorporated into the clinical setting where the distribution, targeting, and persistence of a new generation of therapeutics can be imaged and ultimately guide therapeutic decisions.
Keywords: cell therapy; gene therapy; nuclear imaging; radiotracer.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Peñuelas I., Haberkorn U., Yaghoubi S., Gambhir S.S. Gene therapy imaging in patients for oncological applications. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2005;32(Suppl 2):S384–S403. - PubMed
-
- Basu S., Kwee T.C., Surti S., Akin E.A., Yoo D., Alavi A. Fundamentals of PET and PET/CT imaging. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2011;1228:1–18. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

