Recent advances in the development of nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke
- PMID: 33718667
- PMCID: PMC7905263
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.01.023
Recent advances in the development of nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke
Abstract
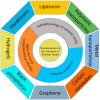
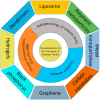
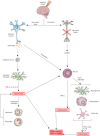
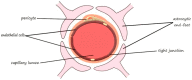
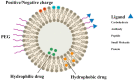
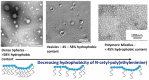
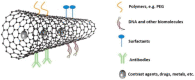
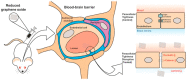
Ischemic stroke is still a serious threat to human life and health, but there are few therapeutic options available to treat stroke because of limited blood-brain penetration. The development of nanotechnology may overcome some of the problems related to traditional drug development. In this review, we focus on the potential applications of nanotechnology in stroke. First, we will discuss the main molecular pathological mechanisms of ischemic stroke to develop a targeted strategy. Second, considering the important role of the blood-brain barrier in stroke treatment, we also delve mechanisms by which the blood-brain barrier protects the brain, and the reasons why the therapeutics must pass through the blood-brain barrier to achieve efficacy. Lastly, we provide a comprehensive review related to the application of nanomaterials to treat stroke, including liposomes, polymers, metal nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, graphene, black phosphorus, hydrogels and dendrimers. To conclude, we will summarize the challenges and future prospects of nanomedicine-based stroke treatments.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Nanomaterials; Stroke.
© 2021 The Authors. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
NO Conflict of Interest.
Figures

References
-
- S H., S S., L L., Stroke Y.C.J. Vol. 48. 2017. pp. 271–275. (Age-period-cohort analysis of stroke mortality in China: data from the global burden of disease study 2013). %A Wang Z. 2. - PubMed
-
- Shichita T. [Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the sterile inflammation after ischemic stroke] Nihon yakurigaku zasshi. Folia pharmacologica Japonica. 2018;151(1):9–14. - PubMed
-
- Lai T.W., Zhang S., Wang Y.T. Excitotoxicity and stroke: identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014;115:157–188. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigo R., Fernandez-Gajardo R., Gutierrez R., Matamala J.M., Carrasco R., Miranda-Merchak A., Feuerhake W. Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: novel therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol. Disord. - Drug Targets. 2013;12(5):698–714. - PubMed
-
- Tang S., He Z., Liang G., Chen S., Ge Y., Sang D.K., Lu J., Lu S., Wen Q., Zhang H. Pulse duration dependent nonlinear optical response in black phosphorus dispersions. Optic Commun. 2018;406:244–248.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

