Three-dimensional (3D) hydrogel serves as a platform to identify potential markers of chondrocyte dedifferentiation by combining RNA sequencing
- PMID: 33718672
- PMCID: PMC7917462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.02.018
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrogel serves as a platform to identify potential markers of chondrocyte dedifferentiation by combining RNA sequencing
Abstract
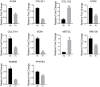
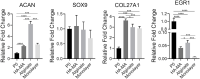
Dedifferentiation of chondrocyte greatly restricts its function and application, however, it is poorly understood except a small number of canonical markers. The non-cell-adhesive property endows polysaccharide hydrogel with the ability to maintain chondrocyte phenotype, which can serve as a platform to identify new molecular markers and therapeutic targets of chondrocyte dedifferentiation. In this study, the high-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was first performed on articular chondrocytes at primary (P0) and passage 1 (P1) stages to explore the global alteration of gene expression along with chondrocyte dedifferentiation. Significantly, several potential marker genes, such as PFKFB3, KDM6B, had been identified via comparatively analyzing their expression in P0 and P1 chondrocytes as well as in 3D constructs (i.e. chondrocyte-laden alginate hydrogel and HA-MA hydrogel) at both mRNA and protein level. Besides, the changes in cellular morphology and enriched pathway of differentially expressed genes during chondrocyte dedifferentiation was studied in detail. This study developed the use of hydrogel as a platform to investigate chondrocyte dedifferentiation; the results provided new molecular markers and potential therapeutic targets of chondrocyte dedifferentiation.
Keywords: Chondrocyte dedifferentiation; Gene expression; Hydrogel; RNA sequencing.
© 2021 [The Author/The Authors].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Blagojevicy M., Jinksy C., Jefferyz A., Jordany K.P. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):24–33. https://doi:10.1016/j.joca.2009.08.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim C., Linsenmeyer K.D., Vlad S.C., Guermazi A., Felson D.T. Prevalence of radiographic and symptomatic hip osteoarthritis in an urban United States community: the framingham osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheum. 2014;66(11):3013–3017. https://doi: 10.1002/art.38795 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Demoor M., Ollitrault D., Gomez-Leduc T., Bouyoucef M., Hervieu M., Fabre H., Lafont J., Denoix J.M., Audigie F., Mallein-Gerin F., Legendre F., Galera P. Cartilage tissue engineering: molecular control of chondrocyte differentiation for proper cartilage matrix reconstruction. Bba-Gen. Subjects. 2014;1840(8):2414–2440. https://doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.02.030 - PubMed
-
- Brittberg M., Lindahl A., Nilsson A., Ohlsson C., Isaksson O., Peterson L. Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;331(14):889–895. https://doi: 10.1056/NEJM199410063311401 - PubMed
-
- Benya P.D., Padilla S.R., Nimni M.E. Independent regulation of collagen types by chondrocytes during the loss of differentiated function in culture. Cell. 1978;15(4):1313–1321. https://doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90056-9 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

