Redox-Responsive Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanogels for the Topical Delivery of the Visual Chromophore to Retinal Photoreceptors
- PMID: 33718708
- PMCID: PMC7948240
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05535
Redox-Responsive Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanogels for the Topical Delivery of the Visual Chromophore to Retinal Photoreceptors
Abstract
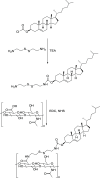
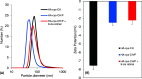
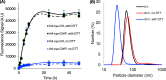
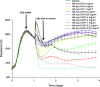
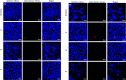
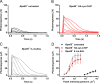
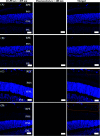
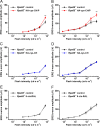
Delivering therapeutics to the posterior segment of the eye is challenging due to various anatomical and physical barriers. While significant improvements have been realized by introducing direct injections to diseased sites, these approaches come with potential side effects that can range from simple inflammation to severe retinal damage. The topical instillation of drugs remains a safer and preferred alternative for patients' compliance. Here, we report the synthesis of penetratin-complexed, redox-responsive hyaluronic acid-based nanogels for the triggered release and delivery of therapeutics to the posterior part of the eye via topical application. The synthesized nanogels were shown to release their load only when exposed to a reducing environment, similar to the cytoplasm. As a model drug, visual chromophore analog, 9-cis-retinal, was loaded into nanogels and efficiently delivered to the mouse retina's photoreceptors when applied topically. Electroretinogram measurements showed a partial recovery of photoreceptor function in all treated eyes versus untreated controls. To the best of our knowledge, this report constitutes the first attempt to use a topically applied triggered-release drug delivery system to target the pigmented layer of the retina, in addition to the first attempt to deliver the visual chromophore topically.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Based Gold Nanoparticles for the Topical Delivery of Therapeutics to the Retina and the Retinal Pigment Epithelium.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;13(19):3324. doi: 10.3390/polym13193324. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641139 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment responsive nanogels as a smart triggered release platform for enhanced intracellular delivery of doxorubicin.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021 Feb;32(3):385-404. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2020.1837504. Epub 2020 Oct 28. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021. PMID: 33054642
-
Penetration Enhancers for Topical Drug Delivery to the Ocular Posterior Segment-A Systematic Review.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Feb 18;13(2):276. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020276. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33670762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucoadhesive and responsive nanogels as carriers for sustainable delivery of timolol for glaucoma therapy.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021 Jan;118:111383. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111383. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 33254990
-
Redox-responsive smart nanogels for intracellular targeting of therapeutic agents: applications and recent advances.J Drug Target. 2019 Apr;27(4):408-422. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2018.1514041. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Drug Target. 2019. PMID: 30124074 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyaluronic Acid Nanogels: A Promising Platform for Therapeutic and Theranostic Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 25;15(12):2671. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122671. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polysaccharide-Based Nanogels to Overcome Mucus, Skin, Cornea, and Blood-Brain Barriers: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Oct 23;15(10):2508. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102508. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-Generation Nanomedicine Approaches for the Management of Retinal Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 22;15(7):2005. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15072005. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanogels-Innovative Drug Carriers for Overcoming Biological Membranes.Gels. 2025 Feb 8;11(2):124. doi: 10.3390/gels11020124. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39996667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Based Gold Nanoparticles for the Topical Delivery of Therapeutics to the Retina and the Retinal Pigment Epithelium.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 28;13(19):3324. doi: 10.3390/polym13193324. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34641139 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

