Advances in emergent biological recognition elements and bioelectronics for diagnosing COVID-19
- PMID: 33718775
- PMCID: PMC7937783
- DOI: 10.1007/s42247-021-00175-9
Advances in emergent biological recognition elements and bioelectronics for diagnosing COVID-19
Abstract
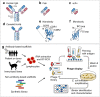
Coronaviruses pose a serious threat to public health. Tremendous efforts are dedicated to advance reliable and effective detection of coronaviruses. Currently, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) diagnosis mainly relies on the detection of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) genetic materials by using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay. However, simpler and more rapid and reliable alternatives are needed to meet high demand during the pandemic. Biosensor-based diagnosis approaches become alternatives for selectively and rapidly detecting virus particles because of their biorecognition elements consisting of biomaterials that are specific to virus biomarkers. Here, we summarize biorecognition materials, including antibodies and antibody-like molecules, that are designed to recognize SARS-CoV-2 biomarkers and the advances of recently developed biosensors for COVID-19 diagnosis. The design of biorecognition materials or layers is crucial to maximize biosensing performances, such as high selectivity and sensitivity of virus detection. Additionally, the recent representative achievements in developing bioelectronics for sensing coronavirus are included. This review includes scholarly articles, mainly published in 2020 and early 2021. In addition to capturing the fast development in the fields of applied materials and biodiagnosis, the outlook of this rapidly evolving technology is summarized. Early diagnosis of COVID-19 could help prevent the spread of this contagious disease and provide significant information to medical teams to treat patients.
Keywords: Antibody; Antibody-like molecule; Biorecognition material; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Virus.
© Qatar University and Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Emerging Biosensors to Detect Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 2;11(11):434. doi: 10.3390/bios11110434. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34821650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The British variant of the new coronavirus-19 (Sars-Cov-2) should not create a vaccine problem.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021 Jan-Feb;35(1):1-4. doi: 10.23812/21-3-E. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021. PMID: 33377359
-
Clinical utility of novel biosensing platform: Diagnosis of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 at point of care.Mater Lett. 2021 Dec 1;304:130612. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130612. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Mater Lett. 2021. PMID: 34381287 Free PMC article.
-
[SARS-CoV-2 and Microbiological Diagnostic Dynamics in COVID-19 Pandemic].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020 Jul;54(3):497-509. doi: 10.5578/mb.69839. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020. PMID: 32755524 Review. Turkish.
-
SPR Based Biosensing Chip for COVID-19 Diagnosis-A Review.IEEE Sens J. 2022 Jun 14;22(14):13800-13810. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3181423. eCollection 2022 Jul. IEEE Sens J. 2022. PMID: 36346093 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Progress in COVID research and developments during pandemic.View (Beijing). 2022 Jul 20:20210020. doi: 10.1002/VIW.20210020. Online ahead of print. View (Beijing). 2022. PMID: 35941909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical biosensors for SARS-CoV-2 detection: Voltametric or impedimetric transduction?Bioelectrochemistry. 2022 Oct;147:108190. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2022.108190. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Bioelectrochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35738049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Biosensors to Detect Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 2;11(11):434. doi: 10.3390/bios11110434. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34821650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impedimetric Sensing: An Emerging Tool for Combating the COVID-19 Pandemic.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 30;13(2):204. doi: 10.3390/bios13020204. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831970 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. 2021 [cited Access January 18, 2021]; Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
