GhPIPLC2D promotes cotton fiber elongation by enhancing ethylene biosynthesis
- PMID: 33718844
- PMCID: PMC7921840
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102199
GhPIPLC2D promotes cotton fiber elongation by enhancing ethylene biosynthesis
Erratum in
-
Erratum: GhPIPLC2D promotes cotton fiber elongation by enhancing ethylene biosynthesis.iScience. 2021 Jun 26;24(7):102737. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102737. eCollection 2021 Jul 23. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34258563 Free PMC article.
Abstract
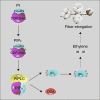
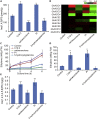
Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) is an important second messenger and one of the products of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC)-mediated phosphatidylinositol (4,5) bisphosphate (PIP2) hydrolysis. However, the function of IP3 in cotton is unknown. Here, we characterized the function of GhPIPLC2D in cotton fiber elongation. GhPIPLC2D was preferentially expressed in elongating fibers. Suppression of GhPIPLC2D transcripts resulted in shorter fibers and decreased IP3 accumulation and ethylene biosynthesis. Exogenous application of linolenic acid (C18:3) and phosphatidylinositol (PI), the precursor of IP3, improved IP3 and myo-inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate (IP6) accumulation, as well as ethylene biosynthesis. Moreover, fiber length in GhPIPLC2D-silenced plant was reduced after exogenous application of IP6 and ethylene. These results indicate that GhPIPLC2D positively regulates fiber elongation and IP3 promotes fiber elongation by enhancing ethylene biosynthesis. Our study broadens our understanding of the function of IP3 in cotton fiber elongation and highlights the possibility of cultivating better cotton varieties by manipulating GhPIPLC2D in the future.
Keywords: biological sciences; plant biology; plant development.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures







References
-
- Abd-El-Haliem A.M., Joosten M.H. Plant phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C at the center of plant innate immunity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2017;59:164–179. - PubMed
-
- Arpat A.B., Waugh M., Sullivan J.P., Gonzales M., Frisch D., Main D., Wood T., Leslie A., Wing R.A., Wilkins T.A. Functional genomics of cell elongation in developing cotton fibers. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004;54:911–929. - PubMed
-
- Blatt M.R., Thiel G., Trentham D.R. Reversible inactivation of K+ channels of Vicia stomatal guard cells following the photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1990;346:766–769. - PubMed
-
- Chu Y.J., Chen X., Xue H.W. Ins(1,4,5)P3 suppresses protein degradation in plant vacuoles by regulating SNX-mediated protein sorting. Mol. Plant. 2016;9:1440–1443. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

