Cytomegalovirus-Specific Immunity Recovers More Slowly after Cord Blood Transplantation Compared with Matched Sibling Donor Allogeneic Transplantation
- PMID: 33718897
- PMCID: PMC7950718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtct.2020.11.014
Cytomegalovirus-Specific Immunity Recovers More Slowly after Cord Blood Transplantation Compared with Matched Sibling Donor Allogeneic Transplantation
Abstract
Background: Rapid quantitative recovery of NK cells but slower recovery of T-cell subsets along with frequent viral infections are reported after umbilical cord blood (UCB) compared with matched sibling donor (MSD) hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). However, it remains unclear whether increased propensity for viral infections is also a result of slower recovery of virus-specific immunity after UCB as compared to MSD HCT.
Objectives: We examined the differences in the function of virus-specific peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) after UCB (N=17) vs. MSD (N=9) using previously collected patient blood samples at various time points after HCT.
Methods: Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) enzyme-linked immune absorbent spot (ELISpot) assay was used to quantify the PBMC frequencies that secrete IFN-γ in response to 11 immunopeptides from 5 common viruses. We included the patients who received the same reduced intensity conditioning regimen without ATG, no systemic glucocorticoids and had no relapse or acute/chronic graft-versus-host disease within 1 year after HCT.
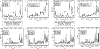
Results: The CMV-reactive PBMC frequencies were higher in CMV seropositive vs. seronegative patients after HCT. Among CMV seropositive patients, the frequency of CMV-reactive PBMC was lower after UCB compared to MSD throughout one year of HCT. We observed no differences in virus-specific PBMC responses towards HHV6, EBV, BK, and adenovirus antigens between UCB and MSD.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that the reconstitution of CMV-specific immunity is slower in CMV seropositive recipients of UCB vs. MSD HCT in contrast to other viruses which had similar recoveries. These study findings support implementation of more potent prophylactic strategies for preventing CMV reactivation in CMV seropositive patients receiving UCB HCT.
Keywords: IFN-γ ELISpot; hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT); immune reconstitution; matched sibling donor (MSD); umbilical cord blood (UCB).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adaptive Natural Killer Cell and Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor-Expressing T Cell Responses are Induced by Cytomegalovirus and Are Associated with Protection against Cytomegalovirus Reactivation after Allogeneic Donor Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015 Sep;21(9):1653-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.05.025. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015. PMID: 26055301 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Delayed immune reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation increases the risks of mortality and chronic GVHD.Blood Adv. 2018 Apr 24;2(8):909-922. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017014464. Blood Adv. 2018. PMID: 29678809 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Reconstitution Profiling Suggests Antiviral Protection after Transplantation with Omidubicel: A Phase 3 Substudy.Transplant Cell Ther. 2023 Aug;29(8):517.e1-517.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2023.04.018. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Transplant Cell Ther. 2023. PMID: 37120136 Clinical Trial.
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
-
[Umbilical cord blood as a source of stem cells].Acta Med Croatica. 2006 Jun;60(3):215-25. Acta Med Croatica. 2006. PMID: 16933834 Review. Croatian.
Cited by
-
Risk Factors for CMV Viremia and Treatment-Associated Adverse Events Among Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021 Dec 16;9(2):ofab639. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofab639. eCollection 2022 Feb. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 35111869 Free PMC article.
-
Durable outcomes of double cord blood transplantation in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: high-risk features for early and long-term mortality.Ther Adv Hematol. 2022 Feb 16;13:20406207221076762. doi: 10.1177/20406207221076762. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Hematol. 2022. PMID: 35186245 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Reconstitution after Haploidentical Donor and Umbilical Cord Blood Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.Life (Basel). 2021 Jan 29;11(2):102. doi: 10.3390/life11020102. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572932 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jacobson CA, Turki AT, McDonough SM, et al. Immune reconstitution after double umbilical cord blood stem cell transplantation: comparison with unrelated peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Biology of blood and marrow transplantation : journal of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 2012;18:565–74. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schmidt-Hieber M, Labopin M, Beelen D, et al. CMV serostatus still has an important prognostic impact in de novo acute leukemia patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Blood 2013;122:3359–64. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
