Effect of Pre-Treatment with a Combination of Fentanyl and Midazolam for Prevention of Etomidate-Induced Myoclonus
- PMID: 33718900
- PMCID: PMC7932701
- DOI: 10.5152/TJAR.2019.90248
Effect of Pre-Treatment with a Combination of Fentanyl and Midazolam for Prevention of Etomidate-Induced Myoclonus
Abstract
Objective: Pre-treatment with either fentanyl or midazolam has previously been used to prevent etomidate-induced myoclonus (EIM). The aim of the present study was to determine the effect of pre-treatment with a combination of midazolam and fentanyl in reducing the incidence and severity of EIM.
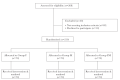
Methods: This prospective, randomised, double-blind study was conducted on 210 surgical patients allocated to three study groups. Group F patients received fentanyl 2 μg kg-1 and 5 mL saline. Group M patients received midazolam 0.03 mg kg-1 and 5 mL saline. Group FM patients received fentanyl 2 μg kg-1 plus midazolam 0.03 mg kg-1. The study drugs were administered intravenously over 30 s. Five minutes after study drug administration, etomidate 0.3 mg kg-1 was administered over 60 s. Patients were observed for 1 min for occurrence and severity of EIM.
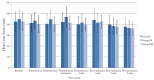
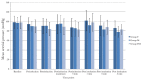
Results: The incidence of EIM was 34/70 (48.6%), 55/70 (78.6%) and 11/70 (15.7%) in groups F, M and FM, respectively (p=0.001). Myoclonus of moderate or severe grade occurred in 23/70 (32.9%), 45/70 (64.3%) and 6/70 (8.6%) in groups F, M and FM, respectively (p=0.001). Patients who experienced myoclonus exhibited a significantly higher percentage change in post-induction heart rate (p=0.02), systolic blood pressure (p=0.001) and mean blood pressure (p=0.001) from pre-induction values than those who did not.
Conclusion: Pre-treatment with a combination of fentanyl and midazolam is more effective than that with fentanyl or midazolam alone in reducing the incidence and severity of EIM. Myoclonus is associated with a higher post-induction haemodynamic variation.
Keywords: Etomidate; fentanyl; midazolam; myoclonus.
© Copyright 2021 by Turkish Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevention of etomidate-induced myoclonus: which is superior: Fentanyl, midazolam, or a combination? A Retrospective comparative study.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Feb 16;20:262-7. doi: 10.12659/MSM.889833. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 24535067 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of remifentanil versus different pharmacological approaches on prevention of etomidate-induced myoclonus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 May 9;13:1593-1607. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S200200. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31190739 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of anesthetic regimens using etomidate and propofol in patients undergoing first-trimester abortions: double-blind, randomized clinical trial of safety and efficacy.Contraception. 2013 Jan;87(1):55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2012.08.014. Epub 2012 Sep 17. Contraception. 2013. PMID: 22995543 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of pretreatment with dexmedetomidine with midazolam for prevention of etomidate-induced myoclonus and attenuation of stress response at intubation: A randomized controlled study.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jan-Mar;34(1):94-98. doi: 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_297_16. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29643630 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dexmedetomidine in preventing etomidate-induced myoclonus: a meta-analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Feb 8;11:365-370. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S121979. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 28223779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The difference in mean arterial pressure induced by remimazolam compared to etomidate in the presence of fentanyl at tracheal intubation: A randomized controlled trial.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 20;14:1143784. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1143784. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37021047 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the effect of ondansetron in reducing myoclonic movements caused by intravenous administration of etomidate.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Apr 30;25(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03099-7. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40307694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Granisetron versus Sufentanil on Reducing Myoclonic Movements Following Etomidate: Double-blind, randomised clinical trial.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2023 Aug;23(3):380-386. doi: 10.18295/squmj.1.2023.009. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2023. PMID: 37655076 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Effectiveness of Various Drug Interventions to Prevent Etomidate-Induced Myoclonus: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 26;9:799156. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.799156. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35559341 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources