Ultrasonography-Guided Oblique Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in Combination with Ultrasonography-Guided Rectus Sheath Block for Anaesthesia in Abdominal Wall Surgery
- PMID: 33718908
- PMCID: PMC7932703
- DOI: 10.5152/TJAR.2020.156
Ultrasonography-Guided Oblique Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in Combination with Ultrasonography-Guided Rectus Sheath Block for Anaesthesia in Abdominal Wall Surgery
Abstract
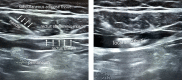
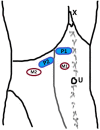
Abdominal wall blocks provide considerable analgesia for relieving post-operative pain. Although they have been performed generally for post-operative pain management, abdominal wall blocks can be used as the principal anaesthesia method in certain cases. In this study, the case of a 47-year-old male patient who underwent surgical excisional biopsy for 2 vague intramuscular mass lesions (was within the rectus abdominis muscle and the other was within the transversus abdominis muscle) was presented. Ultrasonography (USG)-guided oblique subcostal transversus abdominis plane block in combination with USG-guided rectus sheath block was performed successfully as anaesthesia for the abdominal wall surgery. The intervention was performed fully under regional anaesthesia without any need for deep sedation or general anaesthesia.
Keywords: Abdominal wall; oblique subcostal transversus abdominis plane block; pain management; rectus sheath block; regional anaesthesia.
© Copyright 2021 by Turkish Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The author have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-guided continuous oblique subcostal transversus abdominis plane blockade: description of anatomy and clinical technique.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010 Sep-Oct;35(5):436-41. doi: 10.1097/aap.0b013e3181e66702. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010. PMID: 20830871
-
Ultrasound-guided peripheral abdominal wall blocks.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 Jan 20;76:e2170. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2170. eCollection 2021. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 33503184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combination of transversus abdominis plane block and rectus sheath block reduced postoperative pain after splenectomy: a randomized trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2020 Jan 23;20(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12871-020-0941-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 31973700 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transversus Abdominis Plane Block Versus Rectus Sheath Block for Postoperative Pain After Caesarean Delivery: A Randomised Controlled Trial.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2023 Feb;51(1):43-48. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2023.22724. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2023. PMID: 36847318 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the transversus abdominis plane block and its role in postoperative analgesia.Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2014 Jun;28(2):117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 May 9. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2014. PMID: 24993433 Review.
References
-
- Chou R, Gordon DB, de Leon-Casasola OA, Rosenberg JM, Bickler S, Brennan T, et al. Management of Postoperative Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline from the American Pain Society, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Committee on Regional Anesthesia, Executive Committee, and Administrative Council. J Pain. 2016;17:131–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2015.12.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altıparmak B, Korkmaz Toker M, Uysal AI, Kuşçu Y, Gümüş Demirbilek S. Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block versus oblique subcostal transversus abdominis plane block for postoperative analgesia of adult patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Randomized, controlled trial. J Clin Anesth. 2019;57:31–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2019.03.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tulgar S, Kapakli MS, Kose HC, Senturk O, Selvi O, Serifsoy TE, et al. Evaluation of Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block and Oblique Subcostal Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Randomized, Controlled, Prospective Study. Anesth Essays Res. 2019;13:50–6. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_194_18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
