Serum and Cervicovaginal Fluid Antibody Profiling in Herpes Simplex Virus-Seronegative Recipients of the HSV529 Vaccine
- PMID: 33718970
- PMCID: PMC8599754
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab139
Serum and Cervicovaginal Fluid Antibody Profiling in Herpes Simplex Virus-Seronegative Recipients of the HSV529 Vaccine
Abstract
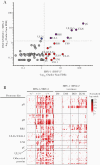
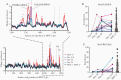
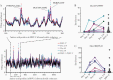
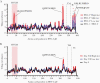
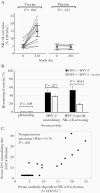
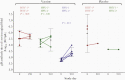
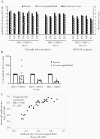
Previous herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) vaccines have not prevented genital herpes. Concerns have been raised about the choice of antigen, the type of antibody induced by the vaccine, and whether antibody is present in the genital tract where infection occurs. We reported results of a trial of an HSV-2 replication-defective vaccine, HSV529, that induced serum neutralizing antibody responses in 78% of HSV-1-/HSV-2- vaccine recipients. Here we show that HSV-1-/HSV-2- vaccine recipients developed antibodies to epitopes of several viral proteins; however, fewer antibody epitopes were detected in vaccine recipients compared with naturally infected persons. HSV529 induced antibodies that mediated HSV-2-specific natural killer (NK) cell activation. Depletion of glycoprotein D (gD)-binding antibody from sera reduced neutralizing titers by 62% and NK cell activation by 81%. HSV-2 gD antibody was detected in cervicovaginal fluid at about one-third the level of that in serum. A vaccine that induces potent serum antibodies transported to the genital tract might reduce HSV genital infection.
Keywords: HSV-2; antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; genital herpes; glycoprotein D; herpes simplex; herpesvirus; replication-defective vaccine; vaccine.
Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2021.
Figures
References
-
- Kohl S. Role of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in neonatal infection with herpes simplex virus. Rev Infect Dis 1991; 13:S950–2. - PubMed
-
- Sullender WM, Miller JL, Yasukawa LL, et al. Humoral and cell-mediated immunity in neonates with herpes simplex virus infection. J Infect Dis 1987; 155:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Prober CG, Sullender WM, Yasukawa LL, Au DS, Yeager AS, Arvin AM. Low risk of herpes simplex virus infections in neonates exposed to the virus at the time of vaginal delivery to mothers with recurrent genital herpes simplex virus infections. N Engl J Med 1987; 316:240–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

