Clinical diagnosis of presumed SOX2 gonadosomatic mosaicism
- PMID: 33719903
- PMCID: PMC8154737
- DOI: 10.1080/13816810.2021.1888127
Clinical diagnosis of presumed SOX2 gonadosomatic mosaicism
Abstract
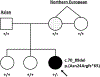
Purpose: To describe a family with presumed SOX2 gonadosomatic mosaicism diagnosed upon ophthalmic examination of the proband's mother.Methods: The family underwent comprehensive ophthalmic and physical examination. Variant detection was performed using trio exome analysis on peripheral leukocyte DNA from blood and saliva samples. Variant segregation analysis was performed using a custom panel NGS sequencing. An identified variant in the SOX2 gene was confirmed in the proband by Sanger sequencing.Results: We report an individual with bilateral microphthalmia, developmental delay, hearing loss, and dysmorphic features. Her mother was found to have asymptomatic forme fruste uveal coloboma affecting her anterior segment. Her father, aunt, and sisters were unaffected. Trio exome sequence analysis showed an apparent de novo heterozygous deletion in the proband, NM_003106.3:c.70_89del, NP_003097.1:p.(Asn24Argfs*65), classified as pathogenic. Testing of the other family members' peripheral blood and saliva was negative for this variant. The iris transillumination abnormalities in the proband's mother supports a gonadosomatic mosaicism scenario.Conclusions: The results from this family underscore the importance of performing detailed evaluations of the parents of apparently sporadically affected individuals with heritable ophthalmic disorders. The identification of mildly affected individuals could substantially alter recurrence risks.
Keywords: SOX2; gonadosomatic; microphthalmia; mosaicism; transillumination.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
