Assessment of Postnatal Corticosteroids for the Prevention of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Neonates: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
- PMID: 33720274
- PMCID: PMC7961472
- DOI: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.6826
Assessment of Postnatal Corticosteroids for the Prevention of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Neonates: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Abstract
Importance: The safety of postnatal corticosteroids used for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) in preterm neonates is a controversial matter, and a risk-benefit balance needs to be struck.
Objective: To evaluate 14 corticosteroid regimens used to prevent BPD: moderately early-initiated, low cumulative dose of systemic dexamethasone (MoLdDX); moderately early-initiated, medium cumulative dose of systemic dexamethasone (MoMdDX); moderately early-initiated, high cumulative dose of systemic dexamethasone (MoHdDX); late-initiated, low cumulative dose of systemic dexamethasone (LaLdDX); late-initiated, medium cumulative dose of systemic dexamethasone (LaMdDX); late-initiated, high cumulative dose of systemic dexamethasone (LaHdDX); early-initiated systemic hydrocortisone (EHC); late-initiated systemic hydrocortisone (LHC); early-initiated inhaled budesonide (EIBUD); early-initiated inhaled beclomethasone (EIBEC); early-initiated inhaled fluticasone (EIFLUT); late-initiated inhaled budesonide (LIBUD); late-initiated inhaled beclomethasone (LIBEC); and intratracheal budesonide (ITBUD).
Data sources: PubMed, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Embase, World Health Organization's International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP), and CINAHL were searched from inception through August 25, 2020.
Study selection: In this systematic review and network meta-analysis, the randomized clinical trials selected included preterm neonates with a gestational age of 32 weeks or younger and for whom a corticosteroid regimen was initiated within 4 weeks of postnatal age. Peer-reviewed articles and abstracts in all languages were included.
Data extraction and synthesis: Two independent authors extracted data in duplicate. Network meta-analysis used a bayesian model.
Main outcomes and measures: Primary combined outcome was BPD, defined as oxygen requirement at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age (PMA), or mortality at 36 weeks' PMA. The secondary outcomes included 15 safety outcomes.
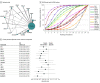
Results: A total of 62 studies involving 5559 neonates (mean [SD] gestational age, 26 [1] weeks) were included. Several regimens were associated with a decreased risk of BPD or mortality, including EHC (risk ratio [RR], 0.82; 95% credible interval [CrI], 0.68-0.97); EIFLUT (RR, 0.75; 95% CrI, 0.55-0.98); LaHdDX (RR, 0.70; 95% CrI, 0.54-0.87); MoHdDX (RR, 0.64; 95% CrI, 0.48-0.82); ITBUD (RR, 0.73; 95% CrI, 0.57-0.91); and MoMdDX (RR, 0.61; 95% CrI, 0.45-0.79). Surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) value ranking showed that MoMdDX (SUCRA, 0.91), MoHdDX (SUCRA, 0.86), and LaHdDX (SUCRA, 0.76) were the 3 most beneficial interventions. ITBUD (RR, 4.36; 95% CrI, 1.04-12.90); LaHdDX (RR, 11.91; 95% CrI, 1.64-44.49); LaLdDX (RR, 6.33; 95% CrI, 1.62-18.56); MoHdDX (RR, 4.96; 95% CrI, 1.14-14.75); and MoMdDX (RR, 3.16; 95% CrI, 1.35-6.82) were associated with more successful extubation from invasive mechanical ventilation. EHC was associated with a higher risk of gastrointestinal perforation (RR, 2.77; 95% CrI, 1.09-9.32). MoMdDX showed a higher risk of hypertension (RR, 3.96; 95% CrI, 1.10-30.91). MoHdDX had a higher risk of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (RR, 5.94; 95% CrI, 1.95-18.11).
Conclusions and relevance: This study suggested that MoMdDX may be the most appropriate postnatal corticosteroid regimen for preventing BPD or mortality at a PMA of 36 weeks, albeit with a risk of hypertension. The quality of evidence was low.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
The Swinging Pendulum of Postnatal Corticosteroid Use.JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Jun 1;175(6):e206842. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.6842. Epub 2021 Jun 7. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33720286 No abstract available.
-
Is a New Era Coming for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Prevention With Corticosteroids?JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Oct 1;175(10):1079. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1858. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34228111 No abstract available.
-
Is a New Era Coming for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Prevention With Corticosteroids?-Reply.JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Oct 1;175(10):1079-1080. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1861. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34228118 No abstract available.
-
EBNEO Commentary: A network meta-analysis of postnatal corticosteroids for bronchopulmonary dysplasia: Has the most appropriate treatment been revealed?Acta Paediatr. 2022 Apr;111(4):903-904. doi: 10.1111/apa.16228. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Acta Paediatr. 2022. PMID: 34989022 No abstract available.
-
Which postnatal corticosteroid regimen is best for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia?J Perinatol. 2022 Dec;42(12):1699-1702. doi: 10.1038/s41372-022-01507-1. Epub 2022 Sep 14. J Perinatol. 2022. PMID: 36104500 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schmidt B, Asztalos EV, Roberts RS, Robertson CM, Sauve RS, Whitfield MF; Trial of Indomethacin Prophylaxis in Preterms (TIPP) Investigators . Impact of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, brain injury, and severe retinopathy on the outcome of extremely low-birth-weight infants at 18 months: results from the Trial of Indomethacin Prophylaxis in Preterms. JAMA. 2003;289(9):1124-1129. doi: 10.1001/jama.289.9.1124 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

