Asexual Experimental Evolution of Yeast Does Not Curtail Transposable Elements
- PMID: 33720342
- PMCID: PMC8233515
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msab073
Asexual Experimental Evolution of Yeast Does Not Curtail Transposable Elements
Abstract
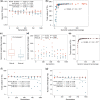
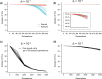
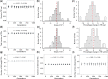
Compared with asexual reproduction, sex facilitates the transmission of transposable elements (TEs) from one genome to another, but boosts the efficacy of selection against deleterious TEs. Thus, theoretically, it is unclear whether sex has a positive net effect on TE's proliferation. An empirical study concluded that sex is at the root of TE's evolutionary success because the yeast TE load was found to decrease rapidly in approximately 1,000 generations of asexual but not sexual experimental evolution. However, this finding contradicts the maintenance of TEs in natural yeast populations where sexual reproduction occurs extremely infrequently. Here, we show that the purported TE load reduction during asexual experimental evolution is likely an artifact of low genomic sequencing coverages. We observe stable TE loads in both sexual and asexual experimental evolution from multiple yeast data sets with sufficient coverages. To understand the evolutionary dynamics of yeast TEs, we turn to asexual mutation accumulation lines that have been under virtually no selection. We find that both TE transposition and excision rates per generation, but not their difference, tend to be higher in environments where yeast grows more slowly. However, the transposition rate is not significantly higher than the excision rate and the variance of the TE number among natural strains is close to its neutral expectation, suggesting that selection against TEs is at best weak in yeast. We conclude that the yeast TE load is maintained largely by a transposition-excision balance and that the influence of sex remains unclear.
Keywords: Saccharomyces cerevisiae; asexual reproduction; excision; mutation accumulation; sexual reproduction; transposon.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures


References
-
- Ågren JA, Greiner S, Johnson MTJ, Wright SI.. 2015. No evidence that sex and transposable elements drive genome size variation in evening primroses. Evolution 69(4):1053–1062. - PubMed
-
- Bartolomé C, Maside X, Charlesworth B.. 2002. On the abundance and distribution of transposable elements in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol. 19(6):926–937. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

