Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiological Insights and Therapeutic Options
- PMID: 33720773
- PMCID: PMC7969169
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050686
Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathophysiological Insights and Therapeutic Options
Abstract
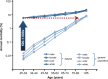
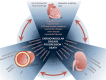
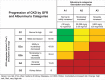
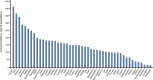
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) exhibit an elevated cardiovascular risk manifesting as coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. Although the incidence and prevalence of cardiovascular events is already significantly higher in patients with early CKD stages (CKD stages 1-3) compared with the general population, patients with advanced CKD stages (CKD stages 4-5) exhibit a markedly elevated risk. Cardiovascular rather than end-stage kidney disease (CKD stage 5) is the leading cause of death in this high-risk population. CKD causes a systemic, chronic proinflammatory state contributing to vascular and myocardial remodeling processes resulting in atherosclerotic lesions, vascular calcification, and vascular senescence as well as myocardial fibrosis and calcification of cardiac valves. In this respect, CKD mimics an accelerated aging of the cardiovascular system. This overview article summarizes the current understanding and clinical consequences of cardiovascular disease in CKD.
Keywords: arrhythmias; cardiovascular disease; chronic kidney disease; clinical aspects; death; heart failure; sudden cardiac.
Figures
References
-
- Stevens PE, O’Donoghue DJ, de Lusignan S, Van Vlymen J, Klebe B, Middleton R, Hague N, New J, Farmer CK. Chronic kidney disease management in the United Kingdom: NEOERICA project results. Kidney Int. 2007;72:92–99. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002273 - PubMed
-
- Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2017;389:1238–1252. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32064-5 - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;325 suppl 3S112–S119. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.1998.v32.pm9820470 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

