A non-parametric method for determining epidemiological reproduction numbers
- PMID: 33721104
- PMCID: PMC7958596
- DOI: 10.1007/s00285-021-01590-6
A non-parametric method for determining epidemiological reproduction numbers
Abstract
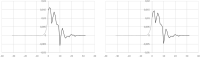
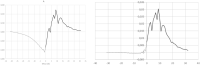
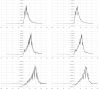
In the spreading of infectious diseases, an important number to determine is how many other people will be infected on average by anyone who has become infected themselves. This is known as the reproduction number. This paper describes a non-parametric inverse method for extracting the full transfer function of infection, of which the reproduction number is the integral. The method is demonstrated by applying it to the timeline of hospitalisation admissions for covid-19 in the Netherlands up to May 20 2020, which is publicly available from the site of the Dutch National Institute of Public Health and the Environment (rivm.nl).
Keywords: Covid-19; Estimation techniques; Infectious diseases; Reproduction number; Transmission.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Parameter estimation from ICC curves.J Biol Dyn. 2021 Dec;15(1):195-212. doi: 10.1080/17513758.2021.1912419. J Biol Dyn. 2021. PMID: 33827379
-
Alternative Strategies for the Estimation of a Disease's Basic Reproduction Number: A Model-Agnostic Study.Bull Math Biol. 2021 Jul 3;83(8):89. doi: 10.1007/s11538-021-00922-3. Bull Math Biol. 2021. PMID: 34216281 Free PMC article.
-
Global dynamics of COVID-19 epidemic model with recessive infection and isolation.Math Biosci Eng. 2021 Feb 22;18(2):1833-1844. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021095. Math Biosci Eng. 2021. PMID: 33757213
-
Airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is the dominant route of transmission: droplets and aerosols.Infez Med. 2021 Mar 1;29(1):10-19. Infez Med. 2021. PMID: 33664169 Review.
-
Ten Epidemiological Parameters of COVID-19: Use of Rapid Literature Review to Inform Predictive Models During the Pandemic.Front Public Health. 2020 Dec 1;8:598547. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.598547. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33335879 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advancements in Defining and Estimating the Reproduction Number in Infectious Disease Epidemiology.China CDC Wkly. 2023 Sep 15;5(37):829-834. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2023.158. China CDC Wkly. 2023. PMID: 37814634 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Analysis of COVID-19 Spread in Tokyo through an Agent-Based Model with Data Assimilation.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 25;11(9):2401. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092401. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566527 Free PMC article.
-
The discrete-time Kermack-McKendrick model: A versatile and computationally attractive framework for modeling epidemics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 28;118(39):e2106332118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106332118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34561307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson R, May R. Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control. Oxford: Oxford Univ Press; 1991.
-
- Blandford RD, McKee CF. Reverberation mapping of the emission line regions of seyfert galaxies and quasars. Astrophys J. 1982;255:419–439. doi: 10.1086/159843. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

