Environmental effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, UV radiation, and interactions with climate change: UNEP Environmental Effects Assessment Panel, Update 2020
- PMID: 33721243
- PMCID: PMC7816068
- DOI: 10.1007/s43630-020-00001-x
Environmental effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, UV radiation, and interactions with climate change: UNEP Environmental Effects Assessment Panel, Update 2020
Abstract
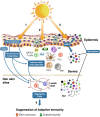
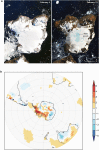
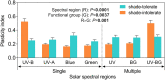
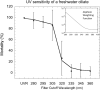
This assessment by the Environmental Effects Assessment Panel (EEAP) of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) provides the latest scientific update since our most recent comprehensive assessment (Photochemical and Photobiological Sciences, 2019, 18, 595-828). The interactive effects between the stratospheric ozone layer, solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and climate change are presented within the framework of the Montreal Protocol and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. We address how these global environmental changes affect the atmosphere and air quality; human health; terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems; biogeochemical cycles; and materials used in outdoor construction, solar energy technologies, and fabrics. In many cases, there is a growing influence from changes in seasonality and extreme events due to climate change. Additionally, we assess the transmission and environmental effects of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, in the context of linkages with solar UV radiation and the Montreal Protocol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bernhard GH, Neale RE, Barnes PW, Neale PJ, Zepp RG, Wilson SR, et al. Environmental effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, UV radiation and interactions with climate change: UNEP Environmental Effects Assessment Panel, update 2019. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences. 2020;19(5):542–584. doi: 10.1039/d0pp90011g. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Polvani LM, Previdi M, England MR, Chiodo G, Smith KL. Substantial twentieth-century Arctic warming caused by ozone-depleting substances. Nature Climate Change. 2020;10(2):130–133. doi: 10.1038/s41558-019-0677-4. - DOI
-
- Wigley TML. Future CFC concentrations under the Montreal Protocol and their greenhouse-effect implications. Nature. 1988;335(6188):333–335. doi: 10.1038/335333a0. - DOI
-
- Myhre G, Shindell D, Bréon FM, Collins W, Fuglestvedt J, Huang J, et al. Anthropogenic and natural radiative forcing. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner GK, Tignor M, Allen SK, Doschung J, et al., editors. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2013. pp. 659–740.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

