Efficacy of linezolid on Treponema pallidum, the syphilis agent: A preclinical study
- PMID: 33721817
- PMCID: PMC7973135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103281
Efficacy of linezolid on Treponema pallidum, the syphilis agent: A preclinical study
Abstract
Background: Penicillin G, the current standard treatment for syphilis, has important drawbacks, but virtually no preclinical or clinical studies have been performed to identify viable alternatives. We tested, both in vitro and in vivo, three marketed antibiotics with adequate pharmacological properties to treat syphilis.
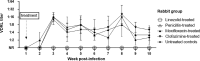
Methods: We used an in vitro culturing system of T. pallidum to perform drug susceptibility testing and applied quantitative PCR targeting the tp0574 gene to measure bacterial growth. To confirm in vivo efficacy, fifteen rabbits were infected intradermally with T. pallidum at eight sites each and randomly allocated to an experimental treatment (linezolid, moxifloxacin, clofazimine) or a control arm (benzathine penicillin G [BPG], untreated). The primary outcome was treatment efficacy defined as the time to lesion healing measured from the date of treatment start. Secondary outcomes were absence of treponemes or treponemal mRNA in injection sites, absence of seroconversion, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) abnormalities and negative rabbit infectivity tests (RIT).
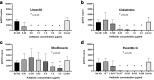
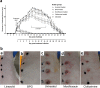
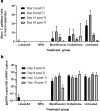
Findings: Linezolid showed in vitro bactericidal activity at concentrations of 0.5 µg/mL or higher. When administered orally to experimentally infected rabbits, it induced healing of early lesions at a time similar to BPG (hazard ratio 3.84; 95% CI 2.05-7.17; p < 0.0001 compared to untreated controls). In linezolid-treated animals, dark-field microscopy and qPCR assessment showed no presence of treponemes after day 3 post-treatment start, serologic test did not convert to positive, CSF had no abnormalities, and RIT was negative. Moxifloxacin and clofazimine failed to inhibit bacterial growth in vitro and could not cure the infection in the rabbit model.
Interpretation: Linezolid, a low-cost oxazolidinone, has in vitro and in vivo activity against T. pallidum, with efficacy similar to BPG in treating treponemal lesions in the animal model. Our findings warrant further research to assess the efficacy of linezolid as an alternative to penicillin G to treat syphilis in human clinical trials.
Funding: European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (Grant agreement No. 850450).
Keywords: Linezolid; Preclinical; Repurposing; Syphilis; Treponema pallidum; Yaws.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hope for new antibiotics for syphilis treatment.EBioMedicine. 2021 Apr;66:103320. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103320. Epub 2021 Apr 1. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 33813132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum: an in-vitro study.Lancet Microbe. 2023 Dec;4(12):e994-e1004. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00219-7. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Lancet Microbe. 2023. PMID: 37827185 Free PMC article.
-
Oral linezolid compared with benzathine penicillin G for treatment of early syphilis in adults (Trep-AB Study) in Spain: a prospective, open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Apr;24(4):404-416. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00683-7. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38211601 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Invasion of the central nervous system by Treponema pallidum: implications for diagnosis and treatment.Ann Intern Med. 1988 Dec 1;109(11):855-62. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-11-855. Ann Intern Med. 1988. PMID: 3056164
-
Biopharmacology of syphilotherapy.J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1976 Dec;3(2 Pt 2):109-27. J Am Vener Dis Assoc. 1976. PMID: 795799 Review.
-
Congenital Syphilis-Comprehensive Narrative Review of Alternative Antibiotic Treatment for Use in Neonates.Sex Transm Dis. 2024 Dec 1;51(12):775-779. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000002057. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Sex Transm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39046152 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal TprK profiling of in vivo and in vitro-propagated Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum reveals accumulation of antigenic variants in absence of immune pressure.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Sep 7;15(9):e0009753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009753. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34492041 Free PMC article.
-
High quality transcriptome profiling confirms the transcriptional landscape of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23272. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06583-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40604007 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum: an in-vitro study.Lancet Microbe. 2023 Dec;4(12):e994-e1004. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00219-7. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Lancet Microbe. 2023. PMID: 37827185 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of transcriptional profiles of Treponema pallidum during experimental infection of rabbits and in vitro culture: Highly similar, yet different.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Sep 27;17(9):e1009949. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009949. eCollection 2021 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34570834 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Horizons in Syphilis Treatment: Challenges, Advances, and Opportunities for Alternative Antibiotics.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025 Mar 13;22(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s11904-025-00725-4. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025. PMID: 40074945 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gerbase AC, Rowley JT, Mertens TE. Global epidemiology of sexually transmitted diseases. Lancet. 1998:351. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Report on global sexually transmitted infection surveillance 2015. WHO Doc Prod Serv Geneva, Switzerland2016.
-
- Collaborators GBD 2017 D and II and P. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1859–1922. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Radolf JD, Lukehart SA. Caister Academic Press; Norfolk, England: 2006. Pathogenic treponema: molecular and cellular biology.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

