The characteristics of circRNA as competing endogenous RNA in pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 33722210
- PMCID: PMC7962291
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08029-7
The characteristics of circRNA as competing endogenous RNA in pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: As one of the novel molecules, circRNA has been identified closely involved in the pathogenesis of many diseases. However, the function of circRNA in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) still remains unknown.
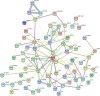
Methods: In the current study, the RNA expression profiles were obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) datasets. The differentially expressed RNAs were identified using R software and the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network was constructed using Cytoscape. Functional and pathway enrichment analyses were performed to identify the candidate circRNA-mediated aberrant signaling pathways. The hub genes were identified by MCODE and CytoHubba plugins of Cytoscape, and then a subnetwork regulatory module was established.
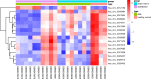
Results: A total of 27 circRNA-miRNA pairs and 208 miRNA-mRNA pairs, including 12 circRNAs, 24 miRNAs and 112 mRNAs were included in the ceRNA network. Subsequently, a subnetwork, including 4 circRNAs, 5 miRNAs and 6 mRNAs, was established based on related circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory modules.
Conclusions: In summary, this work analyzes the characteristics of circRNA as competing endogenous RNA in AML pathogenesis, which would provide hints for developing novel prognostic, diagnostic and therapeutic strategy for AML.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; CircRNA; Competing endogenous RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

