Prime editing in mice reveals the essentiality of a single base in driving tissue-specific gene expression
- PMID: 33722289
- PMCID: PMC7962346
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02304-3
Prime editing in mice reveals the essentiality of a single base in driving tissue-specific gene expression
Abstract
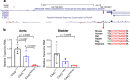
Background: Most single nucleotide variants (SNVs) occur in noncoding sequence where millions of transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) reside. Here, a comparative analysis of CRISPR-mediated homology-directed repair (HDR) versus the recently reported prime editing 2 (PE2) system was carried out in mice over a TFBS called a CArG box in the Tspan2 promoter.
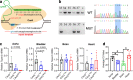
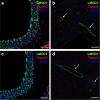
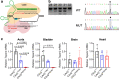
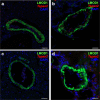
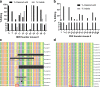
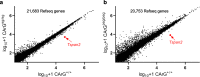
Results: Quantitative RT-PCR showed loss of Tspan2 mRNA in aorta and bladder, but not heart or brain, of mice homozygous for an HDR-mediated three base pair substitution in the Tspan2 CArG box. Using the same protospacer, mice homozygous for a PE2-mediated single-base substitution in the Tspan2 CArG box displayed similar cell-specific loss of Tspan2 mRNA; expression of an overlapping long noncoding RNA was also nearly abolished in aorta and bladder. Immuno-RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization validated loss of Tspan2 in vascular smooth muscle cells of HDR and PE2 CArG box mutant mice. Targeted sequencing demonstrated variable frequencies of on-target editing in all PE2 and HDR founders. However, whereas no on-target indels were detected in any of the PE2 founders, all HDR founders showed varying levels of on-target indels. Off-target analysis by targeted sequencing revealed mutations in many HDR founders, but none in PE2 founders.
Conclusions: PE2 directs high-fidelity editing of a single base in a TFBS leading to cell-specific loss in expression of an mRNA/long noncoding RNA gene pair. The PE2 platform expands the genome editing toolbox for modeling and correcting relevant noncoding SNVs in the mouse.
Keywords: CRISPR; Gene expression; Genome editing; Mouse; Prime editing; Transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
DRL is a consultant and co-founder of Editas Medicine, Pairwise Plants, Beam Therapeutics, and Prime Medicine, companies that use genome-editing technologies. KH, JAW, and APK are employees of Synthego Corporation. CRL and SQT have filed a patent application on CHANGE-seq. SQT is a member of the scientific advisory board of Kromatid.
Figures

References
-
- Studer M, Gavalas A, Marshall H, Ariza-McNaughton L, Rijli FM, Chambon P, Krumlauf R. Genetic interactions between Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 reveal new roles in regulation of early hindbrain patterning. Development. 1998;125:1025–1036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 HL169827/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 15055101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI142756/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118062/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 TR002636/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 HG009490/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147476/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 HL122686/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136224/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UG3TR002636/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

