Tumor mutation burden estimated by a 69-gene-panel is associated with overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 33722306
- PMCID: PMC7962318
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-021-00215-4
Tumor mutation burden estimated by a 69-gene-panel is associated with overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Tumor mutation burden (TMB) as estimated by cancer gene panels (CGPs) has been confirmed to be associated with prognosis and is effective in predicting clinical benefit from immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) in solid tumors. However, whether the TMB calculated by CGPs is associated with overall survival (OS) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is worth exploring.
Methods: The prognostic value of panel-TMB, calculated by a panel of 69 genes (GP69), for 87 DLBCL patients in our clinical center (GDPH dataset) was explored. The results were further validated using 37 DLBCL patients from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database (TCGA dataset).
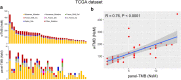
Results: Spearman correlation analysis suggested that panel-TMB is positively correlated with the TMB calculated by whole-exome sequencing (wTMB) in the TCGA dataset (R = 0.76, P < 0.0001). Both GDPH and TCGA results demonstrated that higher panel-TMB is significantly associated with a poor OS for DLBCL patients (P < 0.05) where a panel of 13 genes was associated with poor OS, and another panel of 26 genes was correlated with a favorable OS for DLBCL patients. Further subgroup analysis indicated that higher panel-TMB had shorter OS in DLBCL patients with younger than 60 years, elevated LDH, greater than one extranodal involvement, stage III/IV, an IPI score of 3-5, or HBsAg, anti-HBc, or HBV-DNA negativity (P < 0.05). Interestingly, the nomogram model constructed by panel-TMB, stage, and IPI could individually and visually predict the 1-, 2- and 3-year OS rates of DLBCL patients.
Conclusions: We established GP69 for the evaluation of OS for Chinese DLBCL patients. panel-TMB might be a potential predictor for prognostic stratification of DLBCL patients.
Keywords: Biomarker; Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; Gene panel; Prognosis; TMB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d'Etudes des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. Blood. 2010;116(12):2040–5. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-03-276246. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

