A novel partially open state of SHP2 points to a "multiple gear" regulation mechanism
- PMID: 33722610
- PMCID: PMC8054191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100538
A novel partially open state of SHP2 points to a "multiple gear" regulation mechanism
Abstract
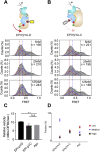
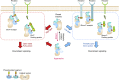
The protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 mediates multiple signal transductions in various cellular pathways, controlled by a variety of upstream inputs. SHP2 dysregulation is causative of different types of cancers and developmental disorders, making it a promising drug target. However, how SHP2 is modulated by its different regulators remains largely unknown. Here, we use single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer and molecular dynamics simulations to investigate this question. We identify a partially open, semiactive conformation of SHP2 that is intermediate between the known open and closed states. We further demonstrate a "multiple gear" regulatory mechanism, in which different activators (e.g., insulin receptor substrate-1 and CagA), oncogenic mutations (e.g., E76A), and allosteric inhibitors (e.g., SHP099) can shift the equilibrium of the three conformational states and regulate SHP2 activity to different levels. Our work reveals the essential role of the intermediate state in fine-tuning the activity of SHP2, which may provide new opportunities for drug development for relevant cancers.
Keywords: allosteric regulation; conformational change; fluorescence resonance energy transfer; single-molecule biophysics; tyrosine-protein phosphatase (tyrosine phosphatase).
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structural reorganization of SHP2 by oncogenic mutations and implications for oncoprotein resistance to allosteric inhibition.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 30;9(1):4508. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06823-9. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30375388 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of activating mutations and allosteric drug inhibition of the phosphatase SHP2.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 30;9(1):4507. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06814-w. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30375376 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the dynamic mechanism of allosteric drug SHP099 inhibiting SHP2E69K.Mol Divers. 2021 Aug;25(3):1873-1887. doi: 10.1007/s11030-020-10179-y. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Mol Divers. 2021. PMID: 33392964
-
Double-edged roles of protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 in cancer and its inhibitors in clinical trials.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Feb;230:107966. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107966. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34403682 Review.
-
Allosteric modulation of SHP2: Quest from known to unknown.Drug Dev Res. 2023 Nov;84(7):1395-1410. doi: 10.1002/ddr.22100. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Drug Dev Res. 2023. PMID: 37583266 Review.
Cited by
-
SHP2 regulates GluA2 tyrosine phosphorylation required for AMPA receptor endocytosis and mGluR-LTD.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 30;121(18):e2316819121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2316819121. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38657042 Free PMC article.
-
Non-ergodicity of a globular protein extending beyond its functional timescale.Chem Sci. 2022 Aug 4;13(33):9668-9677. doi: 10.1039/d2sc03069a. eCollection 2022 Aug 24. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 36091909 Free PMC article.
-
Germline selection of PTPN11 (HGNC:9644) variants make a major contribution to both Noonan syndrome's high birth rate and the transmission of sporadic cancer variants resulting in fetal abnormality.Hum Mutat. 2022 Dec;43(12):2205-2221. doi: 10.1002/humu.24493. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Hum Mutat. 2022. PMID: 36349709 Free PMC article.
-
The Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2: A New Target for Insulin Resistance?Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 31;10(9):2139. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092139. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming Immune Checkpoint Therapy Resistance with SHP2 Inhibition in Cancer and Immune Cells: A Review of the Literature and Novel Combinatorial Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;15(22):5384. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225384. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neel B.G., Gu H., Pao L. The Shp'ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003;28:284–293. - PubMed
-
- Grossmann K.S., Rosário M., Birchmeier C., Birchmeier W. Chapter 2 - the tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 in development and cancer. In: Vande Woude G.F., Klein G., editors. Vol. 106. Elsevier Academic Press; San Diego, CA: 2010. pp. 53–89. (Advances in Cancer Research). - PubMed
-
- Shearer W.T., Rosenwasser L.J., Bochner B.S., Martinez-Moczygemba M., Huston D.P. Biology of common β receptor-signaling cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003;112:653–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

