Transcription initiation mapping in 31 bovine tissues reveals complex promoter activity, pervasive transcription, and tissue-specific promoter usage
- PMID: 33722934
- PMCID: PMC8015843
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.267336.120
Transcription initiation mapping in 31 bovine tissues reveals complex promoter activity, pervasive transcription, and tissue-specific promoter usage
Abstract
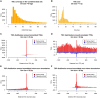
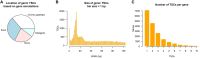
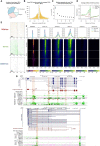
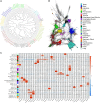
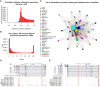
Characterizing transcription start sites is essential for understanding the regulatory mechanisms that control gene expression. Recently, a new bovine genome assembly (ARS-UCD1.2) with high continuity, accuracy, and completeness was released; however, the functional annotation of the bovine genome lacks precise transcription start sites and contains a low number of transcripts in comparison to human and mouse. By using the RAMPAGE approach, this study identified transcription start sites at high resolution in a large collection of bovine tissues. We found several known and novel transcription start sites attributed to promoters of protein-coding and lncRNA genes that were validated through experimental and in silico evidence. With these findings, the annotation of transcription start sites in cattle reached a level comparable to the mouse and human genome annotations. In addition, we identified and characterized transcription start sites for antisense transcripts derived from bidirectional promoters, potential lncRNAs, mRNAs, and pre-miRNAs. We also analyzed the quantitative aspects of RAMPAGE to produce a promoter activity atlas, reaching highly reproducible results comparable to traditional RNA-seq. Coexpression networks revealed considerable use of tissue-specific promoters, especially between brain and testicle, which expressed several genes in common from alternate loci. Furthermore, regions surrounding coexpressed modules were enriched in binding factor motifs representative of each tissue. The comprehensive annotation of promoters in such a large collection of tissues will substantially contribute to our understanding of gene expression in cattle and other mammalian species, shortening the gap between genotypes and phenotypes.
© 2021 Goszczynski et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
