Branched-chain α-ketoacids are preferentially reaminated and activate protein synthesis in the heart
- PMID: 33723250
- PMCID: PMC7960706
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21962-2
Branched-chain α-ketoacids are preferentially reaminated and activate protein synthesis in the heart
Abstract
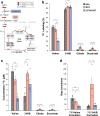
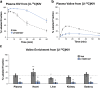
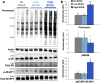
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) and their cognate α-ketoacids (BCKA) are elevated in an array of cardiometabolic diseases. Here we demonstrate that the major metabolic fate of uniformly-13C-labeled α-ketoisovalerate ([U-13C]KIV) in the heart is reamination to valine. Activation of cardiac branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKDH) by treatment with the BCKDH kinase inhibitor, BT2, does not impede the strong flux of [U-13C]KIV to valine. Sequestration of BCAA and BCKA away from mitochondrial oxidation is likely due to low levels of expression of the mitochondrial BCAA transporter SLC25A44 in the heart, as its overexpression significantly lowers accumulation of [13C]-labeled valine from [U-13C]KIV. Finally, exposure of perfused hearts to levels of BCKA found in obese rats increases phosphorylation of the translational repressor 4E-BP1 as well as multiple proteins in the MEK-ERK pathway, leading to a doubling of total protein synthesis. These data suggest that elevated BCKA levels found in obesity may contribute to pathologic cardiac hypertrophy via chronic activation of protein synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
M.W.C., J.T.B., C.D.H., and R.E.G. are employees of Eli Lilly & Co. C.B.N. is a member of the Eli Lilly Global Diabetes Advisory Board. A portion of the work described herein was funded by a sponsored research agreement from Eli Lilly and Co. to C.B.N. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK097441/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR069085/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001271/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK098722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DK126160/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125283/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK124723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK119886/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- L30 HL124508/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL137398/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL135275/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

