RNA N6-methyladenosine: a new player in autophagy-mediated anti-cancer drug resistance
- PMID: 33723389
- PMCID: PMC8110764
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-021-01314-z
RNA N6-methyladenosine: a new player in autophagy-mediated anti-cancer drug resistance
Abstract
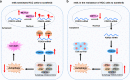
Dysregulation of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is associated with cancer development and progression. The m6A modification plays a crucial role in autophagy regulation precipitating anti-cancer drug resistance. In line with this fact, this commentary discusses m6A modification interfering with autophagy machinery as a major contributing factor for drug resistance in cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

