Nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 Antigen Performed at Point-of-Care Has a High Sensitivity in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Patients With Higher Risk for Transmission and Older Age
- PMID: 33723512
- PMCID: PMC7928615
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofab059
Nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 Antigen Performed at Point-of-Care Has a High Sensitivity in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Patients With Higher Risk for Transmission and Older Age
Abstract
Background: Performance of point-of-care tests in different clinical scenarios and on different samples remains undetermined. We comprehensively evaluated the performance of the nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device.
Methods: This is a prospective study that includes consecutive patients attending 3 primary care centers (PCCs) and an emergency department. The antigen test was performed at point-of-care in nasopharyngeal and nasal swabs and in saliva. Positive percent agreement (PPA) and negative percent agreement (NPA) were calculated with the reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay as reference standard.
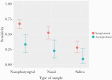
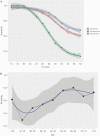
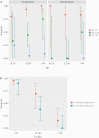
Results: Of 913 patients included, 296 (32.3%) were asymptomatic and 690 (75.6%) came from the PCC. Nasopharyngeal swabs were collected from 913 patients, nasal swabs were collected from 659 patients, and saliva was collected from 611 patients. The RT-PCR was positive in 196 (21.5%) nasopharyngeal samples (NPS). Overall, PPA (95% CI) in NPS was 60.5% (53.3-67.4), and it was lower in nasal swabs (44.7%) and saliva (23.1%). Test performance in NPS was largely dependent on the cycle threshold (Ct) in RT-PCR, with PPA of 94% for Ct ≤25 and 80% for Ct <30. In symptomatic patients, the PPA was 95% for Ct ≤25, 85% for Ct <30, and 89% for the symptom triad of fever, cough, and malaise. Performance was also dependent on age, with a PPA of 100% in symptomatic patients >50 years with Ct <25. In asymptomatic patients, the PPA was 86% for Ct <25. In all cases, NPA was 100%.
Conclusions: The nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 Ag test performed at point-of-care has a good sensitivity in symptomatic patients with Ct <30 and older age. The test was useful to identify asymptomatic patients with lower Ct values.
Keywords: COVID-19; Panbio; SARS-CoV-2; antigen; point-of-care.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

