Modulation of Excitatory Synaptic Transmission During Cannabinoid Receptor Activation
- PMID: 33723716
- PMCID: PMC11421691
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-021-01074-7
Modulation of Excitatory Synaptic Transmission During Cannabinoid Receptor Activation
Abstract
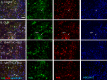
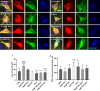
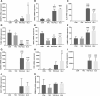
The present research has reported that cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) agonist, delta-(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) modulates synaptogenesis during overexcitation. Microtubule and synaptic distribution, poly(ADP)-ribose (PAR) accumulation were estimated during overexcitation and in the presence of THC. Low concentration of THC (10 nM) increased synaptophysin expression and neurite length, while high concentration of THC (1 µM) induced neurotoxicity. Glutamate caused the loss of neurons, reducing the number and the length of neurites. The high concentration of THC in the presence of glutamate caused the PAR accumulation in the condensed nuclei. Glutamate upregulated genes that are involved in synaptogenesis and excitatory signal cascade. Glutamate downregulated transcription of beta3 tubulin and microtubule-associated protein 2. THC partially regulated gene expression that is implicated in the neurogenesis and excitatory pathways. This suggests that CB1 receptors play a role in neurite growth and the low concentration of THC protects neurons during overexcitation, whereas the high concentration of THC enhances the neurotoxicity.
Keywords: BDNF; Beta tubulin; Cannabinoid receptor; Glutamate; Neurons; Synapses.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures
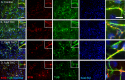
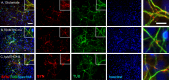
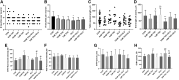
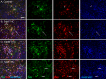
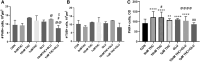
References
-
- Aso E, Fernandez-Duenas V, Lopez-Cano M, Taura J, Watanabe M, Ferrer I, Lujan R, Ciruela F (2019) Adenosine A2A-cannabinoid CB1 receptor heteromers in the hippocampus: cannabidiol blunts delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced cognitive impairment. Mol Neurobiol 56(8):5382–5391. 10.1007/s12035-018-1456-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bukiya AN (2019) Recent advances in cannabinoid physiology and pathology. Adv Exp Med Biol 1162:1–171
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

