Does hydroxychloroquine still have any role in the COVID-19 pandemic?
- PMID: 33724123
- PMCID: PMC7989952
- DOI: 10.1080/14656566.2021.1898589
Does hydroxychloroquine still have any role in the COVID-19 pandemic?
Abstract
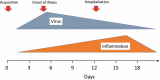
Introduction: The 4-aminoquinolines, chloroquine, and hydroxychloroquine have been used for over 70 years for malaria and rheumatological conditions, respectively. Their broad-spectrum antiviral activity, excellent safety profile, tolerability, low cost, and ready availability made them prime repurposing therapeutic candidates at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.Areas covered: Here, the authors discuss the history of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine, the in vitro data which led to their widespread repurposing and adoption in COVID-19 and their complex pharmacokinetics. The evidence for the use of these drugs is assessed through in vivo animal experiments and the wealth of conflicting data and interpretations published during COVID-19, including the more informative results from randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The safety aspects of these drugs, in particular cardiotoxicity, are then reviewed.Expert opinion: The evidence from clinical trials in COVID-19 supports the well-established safety record of the 4-aminoquinolines at currently recommended dosage. In hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 RCTs show clearly that the 4-aminoquinolines are not beneficial. The only treatments with proven benefit at this stage of infection are immunomodulators (dexamethasone, IL-6 receptor antagonists). No antiviral drugs have proven life-saving in late-stage COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chloroquine; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral; hydroxychloroquine; pharmacokinetics; prevention.
Figures

References
-
- White NJ, Watson JA, Hoglund RM, et al. COVID-19 prevention and treatment: a critical analysis of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine clinical pharmacology. PLoS Med. 2020. September; 17(9):e1003252. - PMC - PubMed
-
• In-depth analysis of clinical pharmacology of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, with a review of toxicity evidence and pharmacokinetic modeling of dosing used in clinical trials in prevention and treatment.
-
- White N, Strub-Wourgraft N, Faiz A, et al. COVID-19 therapeutic reviews and guidelines should not pool evidence from uncomplicated illness in outpatients and severely ill hospitalized patients. Lancet. 2021; 396(10267):1976–1977. In Press.
-
- Boulware DR, Pullen MF, Bangdiwala AS, et al. A randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020. June; 383(6):3. - PMC - PubMed
-
• A well-conducted, randomized controlled trial published early in the pandemic which excluded very large benefits of hydroxychloroquine when given as post-exposure prophylaxis.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
