The Netrin-1-Neogenin-1 signaling axis controls neuroblastoma cell migration via integrin-β1 and focal adhesion kinase activation
- PMID: 33724150
- PMCID: PMC7971226
- DOI: 10.1080/19336918.2021.1892397
The Netrin-1-Neogenin-1 signaling axis controls neuroblastoma cell migration via integrin-β1 and focal adhesion kinase activation
Abstract
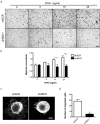
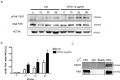
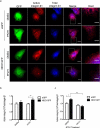
Neuroblastoma is a highly metastatic tumor that emerges from neural crest cell progenitors. Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) is a regulator of cell migration that binds to the receptor Neogenin-1 and is upregulated in neuroblastoma. Here, we show that Netrin-1 ligand binding to Neogenin-1 leads to FAK autophosphorylation and integrin β1 activation in a FAK dependent manner, thus promoting neuroblastoma cell migration. Moreover, Neogenin-1, which was detected in all tumor stages and was required for neuroblastoma cell migration, was found in a complex with integrin β1, FAK, and Netrin-1. Importantly, Neogenin-1 promoted neuroblastoma metastases in an immunodeficient mouse model. Taken together, these data show that Neogenin-1 is a metastasis-promoting protein that associates with FAK, activates integrin β1 and promotes neuroblastoma cell migration.
Keywords: FAK; cell migration; Neogenin-1; Netrin-1; integrin-β1 activation; metastasis; neuroblastoma.
Figures



References
-
- Reymond N, d’Água BB, Ridley AJ. Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(12):858–870. - PubMed
-
- Zent R, Pozzi A, editors. Chapter: Cell-extracellular matrix interactions in cancer. New York: Springer; 2010. p. 1–17
-
- Schaller MD. Cellular functions of FAK kinases: insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 7):1007–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
