Architecture and structural dynamics of the heteromeric GluK2/K5 kainate receptor
- PMID: 33724189
- PMCID: PMC7997659
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66097
Architecture and structural dynamics of the heteromeric GluK2/K5 kainate receptor
Abstract
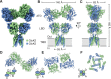
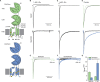
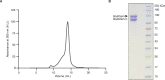
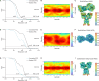
Kainate receptors (KARs) are L-glutamate-gated ion channels that regulate synaptic transmission and modulate neuronal circuits. KARs have strict assembly rules and primarily function as heteromeric receptors in the brain. A longstanding question is how KAR heteromer subunits organize and coordinate together to fulfill their signature physiological roles. Here we report structures of the GluK2/GluK5 heteromer in apo, antagonist-bound, and desensitized states. The receptor assembles with two copies of each subunit, ligand binding domains arranged as two heterodimers and GluK5 subunits proximal to the channel. Strikingly, during desensitization, GluK2, but not GluK5, subunits undergo major structural rearrangements to facilitate channel closure. We show how the large conformational differences between antagonist-bound and desensitized states are mediated by the linkers connecting the pore helices to the ligand binding domains. This work presents the first KAR heteromer structure, reveals how its subunits are organized, and resolves how the heteromer can accommodate functionally distinct closed channel structures.
Keywords: HEK cells; Sf9 cells; baculovirus; human; molecular biophysics; neuroscience; structural biology.
© 2021, Khanra et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NK, PB, AP, DB, JM No competing interests declared
Figures










Similar articles
-
Partial agonism in heteromeric GLUK2/GLUK5 kainate receptor.Proteins. 2025 Jan;93(1):134-144. doi: 10.1002/prot.26565. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Proteins. 2025. PMID: 37526035 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct functional roles of subunits within the heteromeric kainate receptor.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 23;31(47):17113-22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3685-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22114280 Free PMC article.
-
The structural arrangement and dynamics of the heteromeric GluK2/GluK5 kainate receptor as determined by smFRET.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020 Jan 1;1862(1):183001. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020. PMID: 31194959 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from crystal structures of kainate receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Jan;112(Pt A):16-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.05.014. Epub 2016 May 26. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27236079 Review.
-
Structural biology of kainate receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Jun 1;190:108511. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108511. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 33798545 Review.
Cited by
-
Kainate receptor modulation by NETO2.Nature. 2021 Nov;599(7884):325-329. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03936-y. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34552241
-
Trapping of spermine, Kukoamine A, and polyamine toxin blockers in GluK2 kainate receptor channels.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 26;15(1):10257. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54538-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39592599 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Oct;73(4):298-487. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000131. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34753794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial agonism in heteromeric GLUK2/GLUK5 kainate receptor.Proteins. 2025 Jan;93(1):134-144. doi: 10.1002/prot.26565. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Proteins. 2025. PMID: 37526035 Free PMC article.
-
A large-scale curated and filterable dataset for cryo-EM foundation model pre-training.Sci Data. 2025 Jun 7;12(1):960. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05179-2. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40483273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aller MI, Pecoraro V, Paternain AV, Canals S, Lerma J. Increased dosage of High-Affinity kainate receptor gene grik4 alters synaptic transmission and reproduces autism spectrum disorders features. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2015;35:13619–13628. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2217-15.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alt A, Weiss B, Ogden AM, Knauss JL, Oler J, Ho K, Large TH, Bleakman D. Pharmacological characterization of glutamatergic agonists and antagonists at recombinant human homomeric and heteromeric kainate receptors in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 2004;46:793–806. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.11.026. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

