Allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells mitigate acute radiation syndrome by the rescue of damaged bone marrow cells from apoptosis
- PMID: 33724714
- PMCID: PMC8235137
- DOI: 10.1002/sctm.20-0455
Allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells mitigate acute radiation syndrome by the rescue of damaged bone marrow cells from apoptosis
Abstract
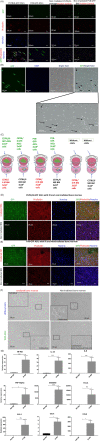
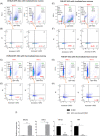
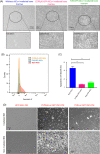
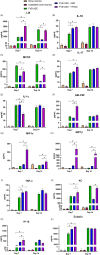
Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) is the radiation toxicity that can affect the hematopoietic, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems upon accidental radiation exposure within a short time. Currently, there are no effective and safe approaches to treat mass population exposure to ARS. Our study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic potential of allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) for total body irradiation (TBI)-induced ARS and understand the underlying mitigation mechanism. We employed 9.25 Gy TBI dose to C57BL/6 mice and studied the effect of allogeneic ASCs on mice survival and regeneration of the hematopoietic system. Our results indicate that intraperitoneal-injected ASCs migrated to the bone marrow, rescued hematopoiesis, and improved the survival of irradiated mice. Our transwell coculture results confirmed the migration of ASCs to irradiated bone marrow and rescue hematopoietic activity. Furthermore, contact coculture of ASCs improved the survival and hematopoiesis of irradiated bone marrow in vitro. Irradiation results in DNA damage, upregulation of inflammatory signals, and apoptosis in bone marrow cells, while coculture with ASCs reduces apoptosis via activation of DNA repair and the antioxidation system. Upon exposure to irradiated bone marrow cells, ASCs secrete prosurvival and hematopoietic factors, such as GM-CSF, MIP1α, MIP1β, LIX, KC, 1P-10, Rantes, IL-17, MCSF, TNFα, Eotaxin, and IP-10, which reduces oxidative stress and rescues damaged bone marrow cells from apoptosis. Our findings suggest that allogeneic ASCs therapy is effective in mitigating TBI-induced ARS in mice and may be beneficial for clinical adaptation to treat TBI-induced toxicities. Further studies will help to advocate the scale-up and adaptation of allogeneic ASCs as the radiation countermeasure.
Keywords: acute radiation syndrome; adipose stem cells; cytokines; hematopoiesis; intraperitoneal injection; total body irradiation.
© 2021 The Authors. STEM CELLS TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cell Therapies for Acute Radiation Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6973. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136973. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rescue from lethal acute radiation syndrome (ARS) with severe weight loss by secretome of intramuscularly injected human placental stromal cells.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018 Dec;9(6):1079-1092. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12342. Epub 2018 Oct 18. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018. PMID: 30334381 Free PMC article.
-
The radiation protection and therapy effects of mesenchymal stem cells in mice with acute radiation injury.Br J Radiol. 2010 Jan;83(985):52-8. doi: 10.1259/bjr/61042310. Br J Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20139249 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Mitigates the Hematopoietic Acute Radiation Syndrome in a Sex- and Strain-dependent Manner in Mice.Health Phys. 2020 Sep;119(3):315-321. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001243. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32175929 Free PMC article.
-
MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: New Emergency Treatment to Limit the Development of Radiation-Induced Hematopoietic Syndrome?Health Phys. 2020 Jul;119(1):21-36. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001264. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32384375 Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like Receptor Agonist CBLB502 Protects Against Radiation-induced Intestinal Injury in Mice.In Vivo. 2024 Jul-Aug;38(4):1636-1648. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13613. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38936936 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide Riboside Improves Stemness of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Inhibits Terminal Adipocyte Differentiation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 10;16(8):1134. doi: 10.3390/ph16081134. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631051 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Therapies for Acute Radiation Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6973. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136973. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin and adipose-derived stem cell combination therapy alleviates radiation-induced skin fibrosis in mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jan 8;15(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03627-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38185658 Free PMC article.
-
Caloric restriction mitigates age-associated senescence characteristics in subcutaneous adipose tissue-derived stem cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 May 9;16(9):7535-7552. doi: 10.18632/aging.205812. Epub 2024 May 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38728252 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

